Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Mov Disord > Volume 13(1); 2020 > Article
-
Case Report
A Case of Abnormal Postures in the Left Extremities after Pontine Hemorrhage: Dystonia or Pseudodystonia? -
Chan Wook Park1
 , Seok Jong Chung1
, Seok Jong Chung1 , Young H. Sohn1
, Young H. Sohn1 , Phil Hyu Lee1,2
, Phil Hyu Lee1,2
-
Journal of Movement Disorders 2020;13(1):62-65.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14802/jmd.19074
Published online: January 31, 2020
1Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Severance Biomedical Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding author: Seok Jong Chung, MD Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 50 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 03722, Korea / Tel: +82-2-2228-5282 / Fax: +82-2-393-0705 / E-mail: pyh6001@hanmail.net
Copyright © 2020 The Korean Movement Disorder Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 4,938 Views
- 130 Download
- 2 Crossref
ABSTRACT
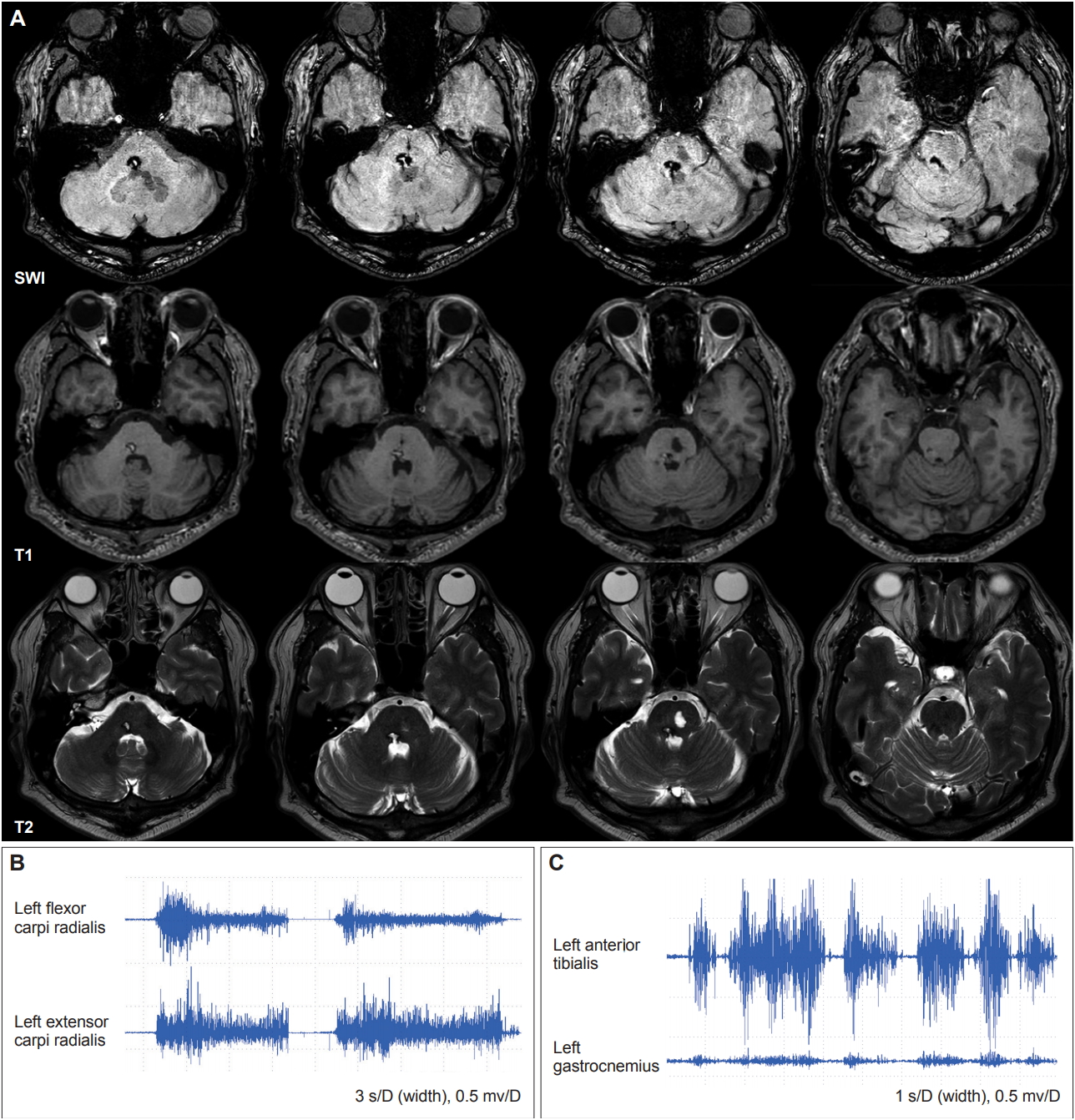
- It is difficult to determine the pathoanatomical correlates of dystonia because of its complex pathophysiology, and most cases with secondary dystonia are associated with basal ganglia lesions. Moreover, it is a challenging issue that patients with abnormal postures accompanied by other neurological findings in the affected body part (e.g., sensory loss) can be diagnosed with true dystonia or pseudodystonia. Here, we report a case of abnormal postures with loss of proprioception in the left extremities after right dorsal pontine hemorrhage.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Video Legend
-
Ethical Statement
The work has been carried out in accordance with the Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki) and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards for experiments involving humans. Informed consent was obtained from all the patients included in the study.
-
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
-
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Seok Jong Chung and Phil Hyu Lee. Data curation: Chan Wook Park. Formal analysis: Chan Wook Park. Funding acquisition: Seok Jong Chung and Phil Hyu Lee. Investigation: Chan Wook Park. Methodology: Chan Wook Park. Supervision: Young H. Sohn. Validation: Seok Jong Chung. Visualization: Chan Wook Park. Writing—original draft: Chan Wook Park. Writing— review & editing: Seok Jong Chung and Phil Hyu Lee.
Notes
- This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (NRF-2016R1A2A2A05920131) and the Ministry of Education (NRF-2018R1D1A1B07048959).
Acknowledgments
| Study | Age/sex | Type of lesion | Site of lesion | Phenomenology | Sensory symptoms | Other clinical symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tan et al. [6] | 43/M | Acute infarction | Left paramedian and ventral pons (old infarction in the left caudate nucleus and putamen) | Right hemidystonia, tonic contractions of the right facial muscle | Normal pin-prick, temperature, and proprioception | Right-sided hemiparesis, dysarthria, right facial upper motor neuron palsy |
| Kim et al. [7] | 75/M | Spontaneous hemorrhage | Left pontine tegmentum extended rostrally to the lower midbrain; an enlarged left anterior inferior medulla with hypertrophic olivary degeneration | Right hand chorea combined with dystonia, oral dyskinesia | Normal sensory exam | Right hemiparesis, dysarthria, horizontal gaze paralysis |
| Loher and Krauss | 31/M | Spontaneous hemorrhage | Right lateral and paramedian tegmentum extending from the pontomedullary junction up to the area of the red nucleus | Left hemidystonia with athetoid movement with rest and postural tremor, cervical dystonia with tremor, right arm bradykinesia | Left-sided hemihypesthesia (unchecked proprioception) | Right 6th and 7th nerve palsies, dysarthria, left-sided hemiparesis, left-sided spasticity |
| 42/F | Posttraumatic hemorrhage | Pontomedullary junction extending from the upper pontine tegmentum to the caudal midbrain (right > left) | Left hemidystonia, cervical dystonia | Left-sided hemihypesthesia (unchecked proprioception) | Restricted upward and horizontal conjugate gaze, dysarthria, mild tetraplegia, limb ataxia (right > left), truncal ataxia, unstable gait | |
| 4/M | Diffuse axonal injury after head trauma | Left lateral pontomesencephalic tegmentum, extended from the mid-pons to the posterior red nucleus | Right hemidystonia with tremor, torticollis, right arm bradykinesia | Right-sided hemihypesthesia | Right 7th nerve palsy, right-sided spastic hemiparesis, right arm ataxia |
- 1. Albanese A, Bhatia K, Bressman SB, Delong MR, Fahn S, Fung VS, et al. Phenomenology and classification of dystonia: a consensus update. Mov Disord 2013;28:863–873.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Phukan J, Albanese A, Gasser T, Warner T. Primary dystonia and dystonia-plus syndromes: clinical characteristics, diagnosis, and pathogenesis. Lancet Neurol 2011;10:1074–1085.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Balint B, Mencacci NE, Valente EM, Pisani A, Rothwell J, Jankovic J, et al. Dystonia. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018;4:25.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Jinnah HA, Neychev V, Hess EJ. The anatomical basis for dystonia: the motor network model. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y) 2017;7:506.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Berlot R, Bhatia KP, Kojović M. Pseudodystonia: a new perspective on an old phenomenon. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2019;62:44–50.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Tan EK, Chan LL, Auchus AP. Hemidystonia precipitated by acute pontine infarct. J Neurol Sci 2005;234:109–111.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Kim HJ, Cho YJ, Cho JY, Hong KS, Jeon BS. Choreodystonia in a patient with hypertrophic olivary degeneration after pontine tegmental hemorrhage. Mov Disord 2008;23:920–922.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Loher TJ, Krauss JK. Dystonia associated with pontomesencephalic lesions. Mov Disord 2009;24:157–167.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Desrochers P, Brunfeldt A, Sidiropoulos C, Kagerer F. Sensorimotor control in dystonia. Brain Sci 2019;9:pii: E79.Article
- 10. Avanzino L, Fiorio M, Conte A. Actual and illusory perception in Parkinson’s disease and dystonia: a narrative review. Front Neurol 2018;9:584.ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Rehabilitation of hemidystonia as a result of right pontine hemorrhagic stroke
Melanie Aing, Craig DiTommaso
The Journal of the International Society of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine.2023; 6(4): 116. CrossRef - Hemidystonia after Pontine Hemorrhage Successfully Treated with Pharmacotherapy and Intensive Rehabilitation: a Case Report
Gyu Seong Kim, Yeon Gyu Jeong, Yoon Jeong Jeong, Seo Yeon Yoon
Brain & Neurorehabilitation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
Comments on this article
 KMDS
KMDS
 E-submission
E-submission
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

