Apomorphine Monotherapy for Parkinson’s Disease: A Neglected Option?
Article information
Dear Editor,
Continuous subcutaneous apomorphine infusion (CSAI) is a safe and effective way of reducing off time in patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD) whose motor complications are suboptimally controlled by oral medication [1] and treating severe insomnia in patients with fluctuating PD [2]. Uncontrolled studies have also indicated that the benefits of CSAI are sustained over time [3]. However, CSAI monotherapy use has only been reported among a limited number of patients [3-10] and rarely as a strict monotherapy [6,9] (i.e., without quick-start levodopa in the morning or controlled-release levodopa at night). Furthermore, long-term therapeutic benefits (> 10 years) have not been reported to date. Here, we report a unique case of strict CSAI monotherapy maintained for 12 years.
The patient was a 57-year-old woman with a 16-year history of typical young-onset PD. She had gradually developed classic motor complications, including fluctuations with severe wearing off associated with off time freezing of gait and moderate to severe peak-dose dyskinesia. She also had severe insomnia but no cognitive alteration, hallucinations, or psychiatric disorders. At this stage, her daily daytime medication consisted of 16 mg of ropinirole, 175/800 mg of carbidopa/levodopa, 1,200 mg of entacapone, and 400 mg of amantadine.
As the patient was reluctant to undergo deep brain stimulation, we decided to initiate CSAI 24 h a day with concomitant reduction of oral treatment. After 3 months, she was no longer taking oral medication, and the daily dose of apomorphine was 168 mg. We then gradually adjusted the daily dose according to the patient’s feedback to reach 192 mg at 6 months and eventually 201 mg 14 months after CSAI initiation (flow = 9.2 mg/h in the daytime and 7.5 mg/h at nighttime) (Figure 1A). The maintenance daily dose remains similar 12 years later.
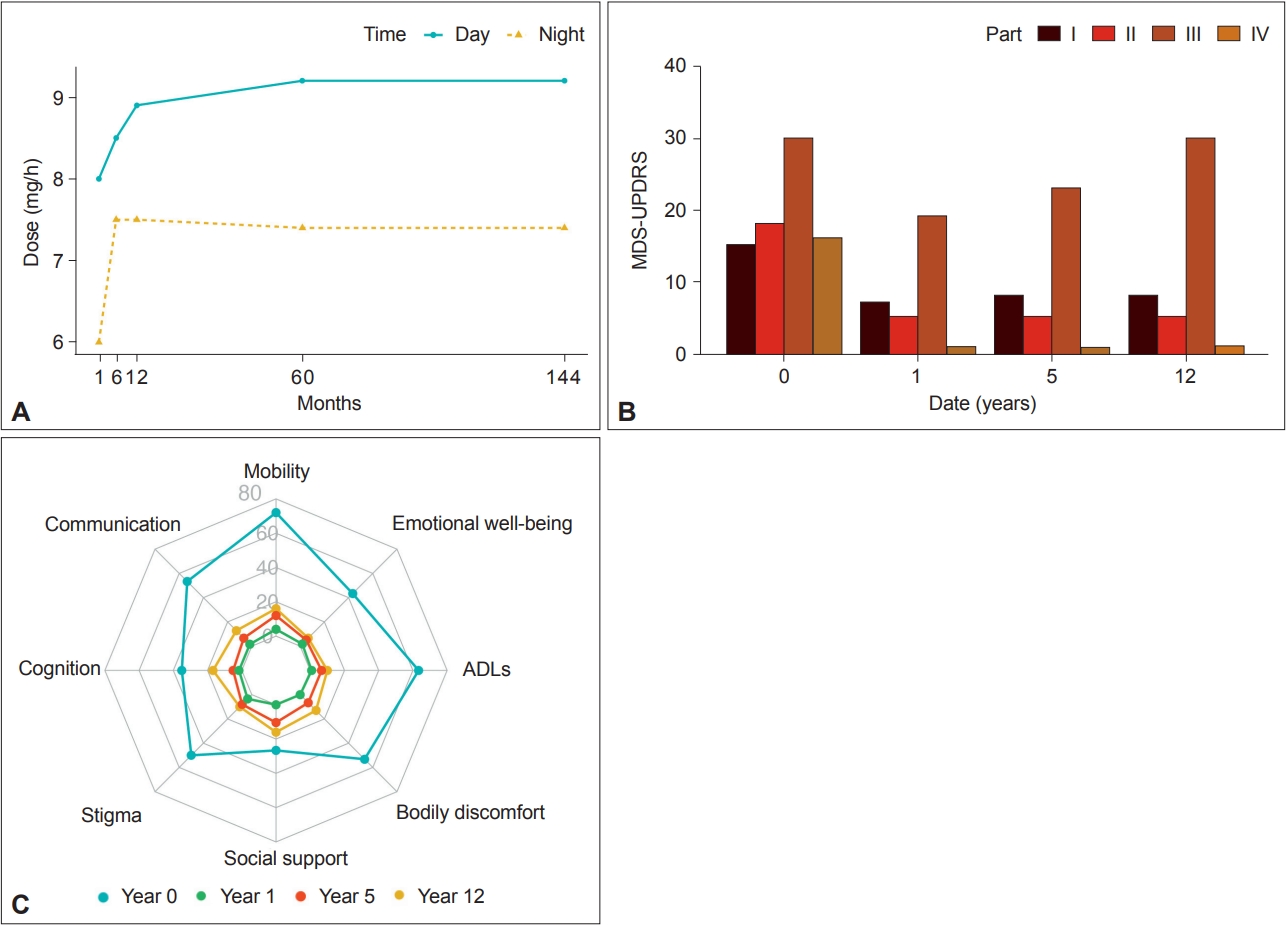
Effects of continuous subcutaneous apomorphine infusion on motor complications (Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale [UPDRS]) and quality of life (Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire-39 [PDQ-39]). A: Titration of continuous subcutaneous apomorphine infusion dose over 12 years. B: Evolution of UPDRS at different time points showing a dramatic and persistent improvement in motor fluctuations (part IV) over time. C: Evolution of PDQ-39 scores over time. MDS-UPDRS, Movement Disorder Society-Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale; ADLs, activities of daily living.
Since the introduction of CSAI, the patient has exhibited remarkable improvement in her motor complications with no dyskinesia, no off periods, and normal sleep. The effects of CSAI on motor complications (Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale [UPDRS]) and quality of life (Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire-39 [PDQ-39]) were evaluated at 1 year, 5 years and 12 years (Figure 1B and C). After a few weeks, she could manage the pump device without the help of a caregiver, and she has never complained of major side effects related to apomorphine. Her current motor condition 28 years after disease onset is shown in an illustrative homemade video (Supplementary Video 1 in the online-only Data Supplement).
In this study, we report the case of a patient with severe motor complications 16 years after PD onset who showed major improvement in both motor fluctuations and dyskinesia with strict high-dose CSAI monotherapy. Our case is original in various aspects: 1) the improvement was sustained over 12 years; 2) we used strict monotherapy without any oral levodopa intake; 3) CSAI was administered 24 h a day; and 4) daily doses were high (approximately 200 mg) and well tolerated.
CSAI is an effective and safe treatment for clinical motor fluctuations that persist despite optimized oral or transdermal medication in patients with advanced PD. Expert consensus recommends simultaneously reducing the levodopa dose for better control of dyskinesia, but without complete withdrawal, and only discontinuing dopamine agonists, monoamine oxidase-B (MAO-B) inhibitors, catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) inhibitors, amantadine, and anticholinergics when appropriate. To date, CSAI monotherapy has only been reported in a total of 112 patients, with no detailed report of long-term follow-up (> 10 years) for an individual patient [3-10].
One large retrospective study focused on apomorphine monotherapy for treating refractory motor complications of PD [4]. In the study, 45 patients were followed up for a mean duration of 33.8 months. The results indicated that CSAI monotherapy (mean daily dose of 103 mg) can improve both refractory off periods and peak-dose dyskinesia. The patients (mean age of 59 years) had a mean PD duration of 16 years and a mean daily levodopa dose at baseline of 853 mg. Our patient resembles those of this series in terms of age, disease duration, and levodopa daily dose before CSAI initiation. The most striking difference was that we used a higher dose of apomorphine. The magnitude of the effect we observed on motor complications, especially on peak-dose dyskinesia, was greater than the mean effect reported in this series. Of note, when used as add-on treatment, the positive effect on dyskinesia is lesser and tends to fade over time [3]. We hypothesized that this could possibly be related to this differential approach, namely, high-dose CSAI monotherapy. In the literature, reported apomorphine doses ranged from 90.6 to 106.1 mg for 101 patients treated with monotherapy during waking hours and were not reported for the 11 patients with 24-hour CSAI monotherapy (no details about the dose) [3-10]. For our patient, CSAI was administered 24 h a day at a higher daily dose, i.e., approximately 200 mg.
Although 24-hour CSAI monotherapy (or waking time CSAI monotherapy) has not been formally compared to the add-on option, we can speculate about the possible advantages and disadvantages of this dosing regimen based on our observations and general knowledge of CSAI. The two main advantages of 24-hour CSAI monotherapy could be the possibility of achieving sustained control of dyskinesia and a sizeable beneficial effect on nonmotor symptoms, especially on sleep disorders [2,4,11]. Conversely, patients with high-dose 24-hour CSAI monotherapy may have a greater risk of side effects such as skin nodules, digestive symptoms, orthostatic hypotension, and neuropsychiatric manifestations [3-6,8-10]. These side effects are frequent reasons for early discontinuation of CSAI and may therefore limit its use [3,12].
The pathogenesis of dyskinesia is complex and not fully understood. Our paradigmatic observation suggests that the suppression of pulsatile dopaminergic stimulation could reverse the postsynaptic plastic changes involved in the generation of levodopa-induced dyskinesia.
Beyond this pathophysiological proof of concept, our report also provides important information about a second-line treatment strategy for fluctuating PD. High-dose CSAI monotherapy can be a highly effective option for some patients who are eligible for deep brain stimulation but reluctant to undergo surgical treatment, such as our patient. Although potentially more effective than the add-on option, our experience is that the use of strict CSAI monotherapy/high-dose CSAI is often associated with side effects, restricting its use to a small proportion of fluctuating PD patients in clinical practice.
Supplementary Material
The online-only Data Supplement is available with this article at https://doi.org/10.14802/jmd.23057.
Video 1.
The video illustrates the motor condition of the patient in her usual daily life activities 12 years after disease onset when treated with apomorphine infusion.
Notes
Ethics Statement
Informed oral and written consent was obtained from the patient included in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
David Devos served on advisory boards, served as a consultant and given lectures for pharmaceutical companies such as Abbvie, Alterity, Orkyn, Air Liquide, Elivie, Home perf, Apopharma, Lundbeck, Everpharma, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Ever pharma, Boston Scientific, UCB pharma, EISAI, Servier, PTC Therapeutics, Orion, AB science, Alzprotect, Cajal Neuroscience, and Cure Parkinson Trust. He holds stakes in InBrain Pharma and Invenis biotherapies.
Emmanuel Roze received honorarium for speech from Orkyn, Aguettant, and Elivie. He received research support from Orkyn, Aguettant, Elivie, Ipsen, and Everpharma.
The other authors declare that there are no additional disclosures to report.
Funding Statement
None
Author contributions
Conceptualization: all authors. Data curation: Clément Desjardins, Emmanuel Roze. Formal analysis: Clément Desjardins. Investigation: Clément Desjardins, Emmanuel Roze. Methodology: Clément Desjardins, Emmanuel Roze. Supervision: Emmanuel Roze. Validation: Clément Desjardins, Emmanuel Roze. Writing—original draft: Clément Desjardins, Emmanuel Roze. Writing—review & editing: all authors.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patient who contributed to this report.
