Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Mov Disord > Volume 2(2); 2009 > Article
-
Case Report
A Case of Painful Hemimasticatory Spasm with Masseter Muscle Hypertrophy Responsive to Botulinum Toxin - Jin-Hyuck Kima, Seok-Won Hanb, Yun Joong Kimb, Jooyong Kimb, Mi-Suh Ohb, Hyeo-Il Mab, Byung-Chul Leeb
-
Journal of Movement Disorders 2009;2(2):95-97.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14802/jmd.09026
Published online: October 30, 2009
aDepartment of Neurology, Keyo Medical Foundation Keyo Hospital, Uiwang, Korea
bDepartment of Neurology, Hallym University, College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea
- Corresponding author: Hyeo-Il Ma, MD, PhD, Department of Neurology, Hallym University, College of Medicine, 896 Pyeongchon-dong, Dongan-gu, Anyang 431-070, Korea, Tel +82-31-380-3742, Fax +82-31-381-4659, E-mail hima@hallym.ac.kr
• Received: October 9, 2009 • Revised: October 23, 2009 • Accepted: November 6, 2009
Copyright © 2009 The Korean Movement Disorder Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 52,947 Views
- 84 Download
- 6 Crossref
ABSTRACT
- Hemimasticatory spasm (HMS) is a rare disorder of the trigeminal nerve characterized by paroxysmal involuntary contractions of the unilateral jaw-closing muscles. HMS has been frequently described in association with facial hemiatrophy or localized scleroderma. A 42-year-old female presented with involuntary paroxysmal spasms of the left face, of 6 months duration. Her lower face on the left was markedly hypertrophied without skin lesions. An electrophysiological study indicated that the masseter reflexes and masseteric silent period were attenuated on the affected side. Surface electromyography demonstrated irregular bursts of motor unit potentials at high frequencies up to 200 Hz. Magnetic resonance imaging of the head showed marked hypertrophy of the left masseter muscle. Biopsy of the hypertrophied masseter muscle was normal. Repeated local injections of botulinum toxin noticeably reduced the size of the hypertrophied muscle as well as improved the patient’s symptoms.
- A 42-year-old female presented with involuntary paroxysmal spasms of the left masticatory muscle, of 6 months duration. The spasms were mild in the early stage; however, they increased gradually in duration and frequency. The spasms were frequently painful and sometimes awoke her from sleep. The lower half of the face on the left side hypertrophied over time. She had no specific medical diseases.
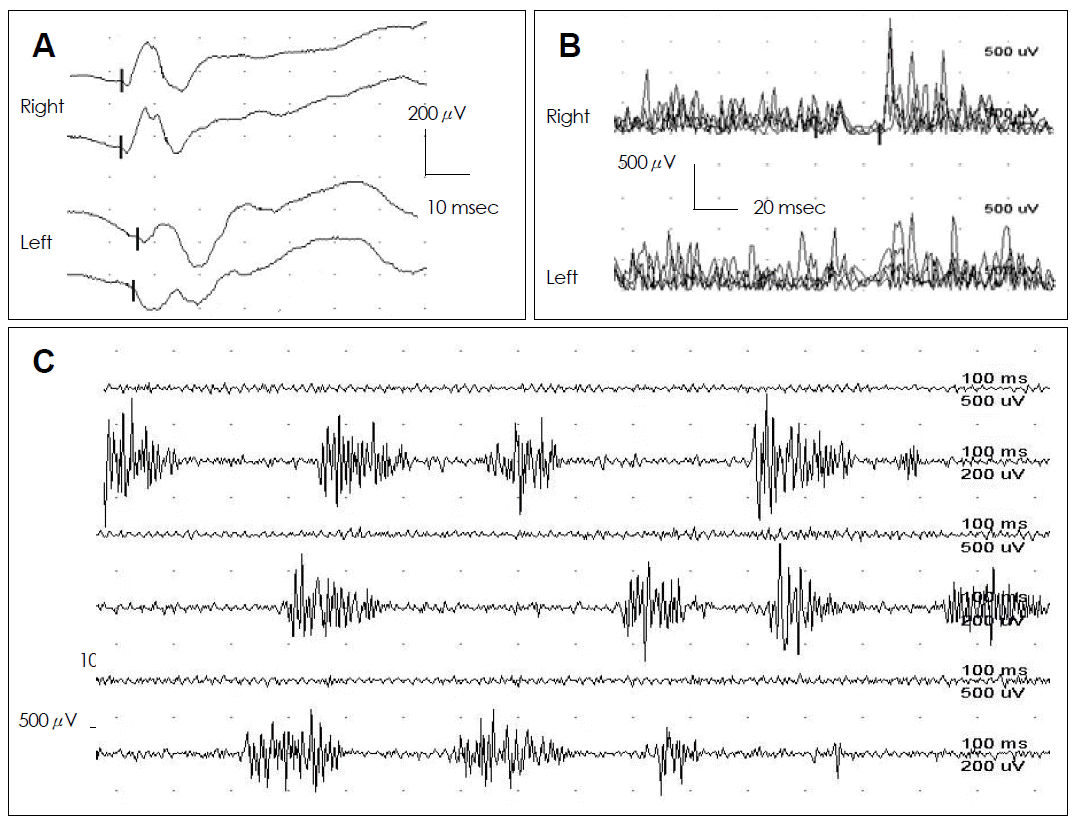
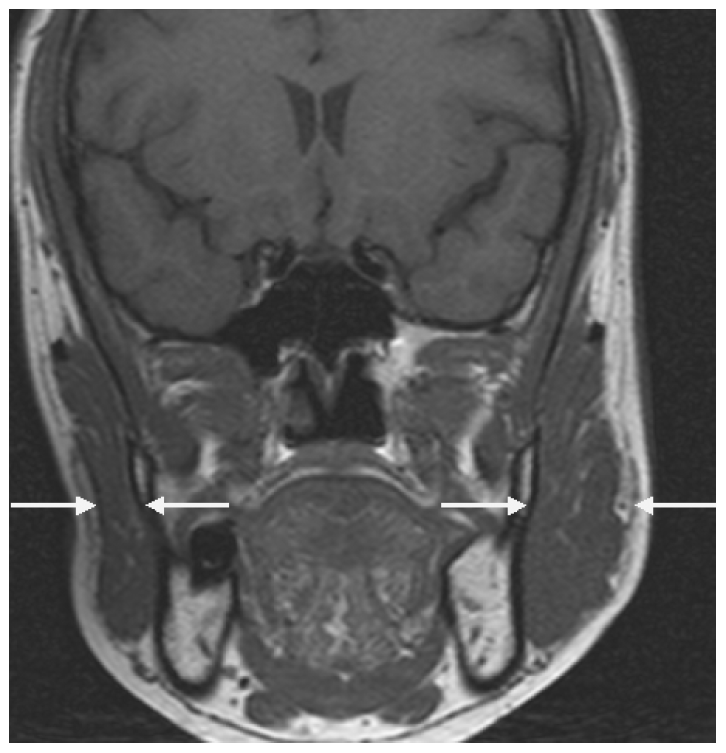
- On admission, her masseter muscle on the left was markedly hypertrophied. However, neither FHA nor a skin lesion was noticed. The spasms usually continued for about 10 seconds, but sometimes lasted for up to a few minutes. Neurologic examinations, including masticatory muscle function and jaw jerk, were normal. Hematological, biochemical, and serologic tests, including antinuclear antibody, rheumatoid factor, anti-DNA antibody, and C-reactive protein, were normal. The blink reflex was normal on an electrophysiological study. Masseter reflexes elicited by tapping her chin and recorded by surface electrodes from the masseter muscle showed delayed latencies and decreased amplitudes on the left side during the spasm episodes (Figure 1A). Moreover, the masseteric silent period was attenuated on the affected side (Figure 1B). Surface electromyography demonstrated irregular bursts of motor unit potentials at 50 to 200 Hz during the period of involuntary spasm or at random intervals (Figure 1C). Magnetic resonance imaging of the head showed pronounced hypertrophy of the left masseter muscle (Figure 2). A muscle biopsy done at the central region of the hypertrophied muscle revealed nonspecific results.
- The frequency of the spasm and pain improved slightly after treatment with phenytoin. Several local injections of 20–50 units of botulinum toxin in the left masseter muscle led to marked improvement of her symptoms. After 3 months, the hypertrophy of the masseter muscle was substantially decreased (Figure 3). The benefits of the botulinum toxin injections persisted for 4 months, and subsequent injections were performed with equal success. The follow-up electrophysiological profiles were also improved.
Case Report
- Since the first reported description of the electrophysiological and clinical features of HMS with FHA,1 about 20 cases have been described. HMS predominantly affects women in the third to fourth decades and is associated with hemiatrophy in two-thirds and scleroderma in one-third.2–4 The spasm affects the masseter muscle most frequently and may involve one or more jaw-closing muscles.2,3,8,9 However, the involvement of jaw openers has never been described.2,3,8
- Although the pathophysiology of HMS is not well known, peripheral lesion of the trigeminal motor nerve is considered to play a role.2–7 It has been proposed that HMS is produced by ectopic discharge secondary to focal demyelination of the trigeminal motor fiber caused by compression, entrapment, or stretching injury to the extracranial portion of the nerve.2–5,8,9 Some authors have postulated that HMS might originate from vascular compression of the trigeminal motor nucleus or the motor root near the brainstem.2,3,5,9 However, evidence of vascular compression has not been demonstrated in surgical explorations.3–5
- Medications such as carbamazepine, phenytoin, and clonazepam may be helpful, although the effect of treatment with these drugs has been insufficient in most patients with HMS.3,5,7,8 In our case, phenytoin was beneficial to only a limited degree for improving pain and the frequency of the spasms. On the other hand, the local injections of botulinum toxin resolved the spasms and reduced the muscle hypertrophy. In our search of the literature, another eight patients with HMS received treatment with botulinum toxin, and all of them showed an excellent response to this therapy (Table 1).2–5,7–9 All of the cases except two7,9 were associated with muscle hypertrophy. The reports all described obtaining marked improvements in the pain and spasms; however, an effect on the muscle hypertrophy was not mentioned in the previous cases. Our case clearly demonstrated a regression in the size of the hypertrophied muscle.
- In this study, we presented a case of HMS associated with masseter muscle hypertrophy and related the electrophysiological and neuroimaging findings. Botulinum toxin may be considered the treatment of choice for pain and spasm in HMS. In addition, this therapy can be helpful for decreasing the size of the hypertrophied muscle.
Discussion
Figure 1.Electrophysiologic studies in this patient. A: Masseter reflexes show delayed latency and decreased amplitude on the left side during the spasm episodes. B: The masseteric silent period is attenuated on the affected side. C: Surface electromyography demonstrates irregular bursts of motor unit potentials at 50 to 200 Hz during the period of involuntary spasm.
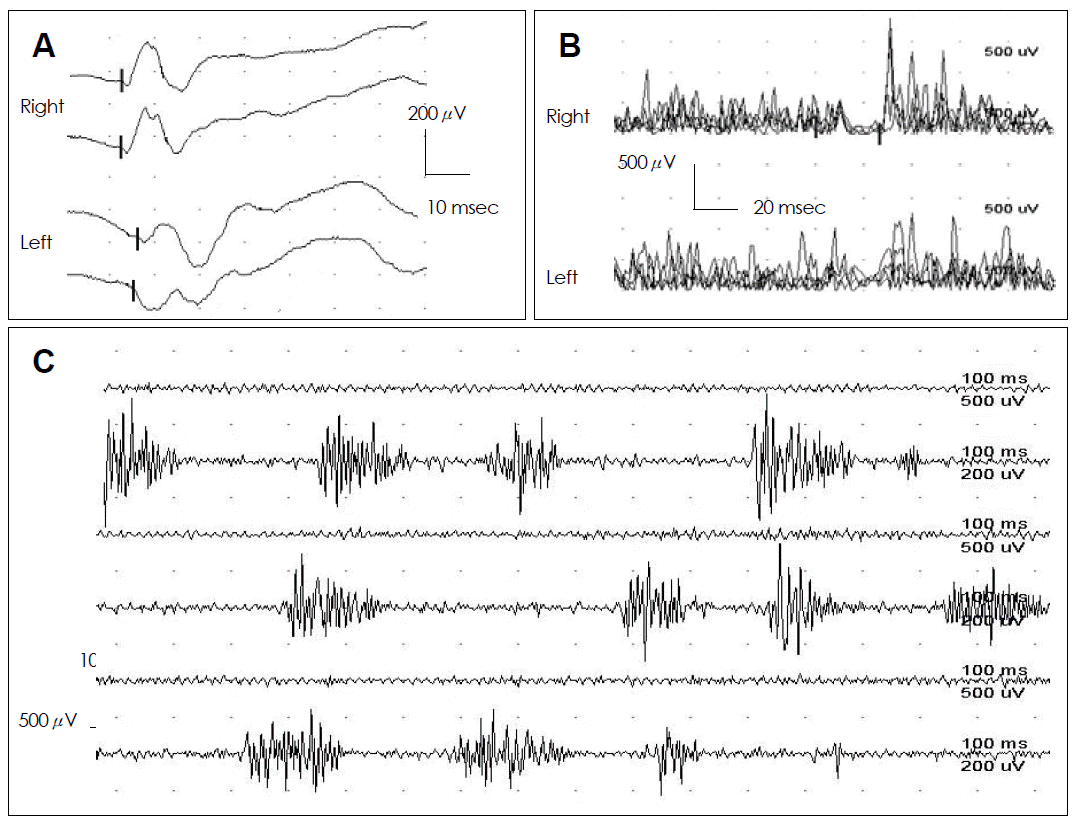

Figure 2.On T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging before treatment with botulinum toxin, hypertrophy of the left masseter muscle is noted.
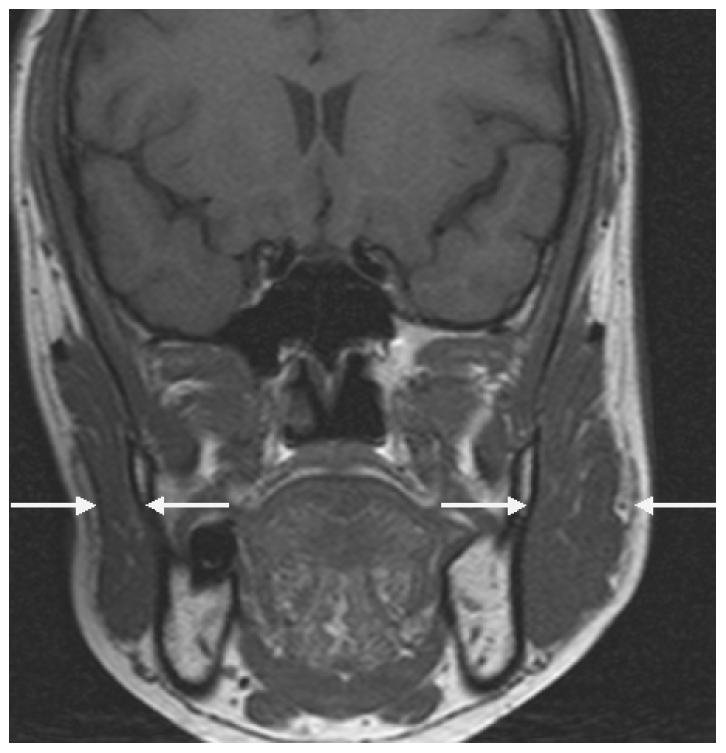

Figure 3.Hypertrophy of the left face in this patient before (A) and after 3 months (B) of botulinum toxin injections.
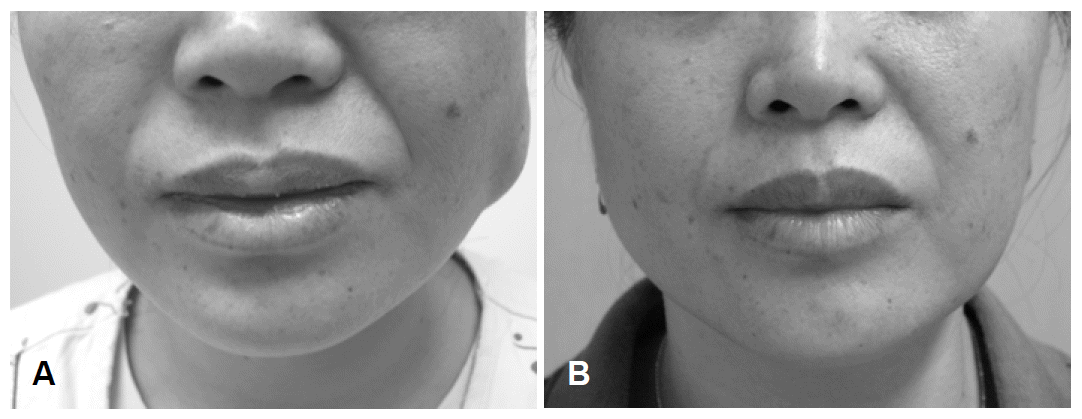

Table 1.Summary of reported cases of HMS treated with botulinum toxin
- 1. Kaufman MD. Masticatory spasm in facial hemiatrophy. Ann Neurol 1980;7:585–587.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Kim HJ, Jeon BS, Lee KW. Hemimasticatory spasm associated with localized scleroderma and facial hemiatrophy. Arch Neurol 2000;57:576–580.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Cruccu G, Inghilleri M, Berardelli A, Pauletti G, Casali C, Coratti P, et al. Pathophysiology of hemimasticatory spasm. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1994;57:43–50.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Ebersbach G, Kabus C, Schelosky L, Terstegge L, Poewe W. Hemimasticatory spasm in hemifacial atrophy: diagnostic and therapeutic aspects in two patients. Mov Disord 1995;10:504–507.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Auger RG, Litchy WJ, Cascino TL, Ahlskog JE. Hemimasticatory spasm: clinical and electrophysiologic observations. Neurology 1992;42:2263–2266.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Esteban A, Traba A, Prieto J, Grandas F. Long term follow up of a hemimasticatory spasm. Acta Neurol Scand 2002;105:67–72.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Mir P, Gilio F, Edwards M, Inghilleri M, Bhatia KP, Rothwell JC, et al. Alternation of central motor excitability in a patient with hemimasticatory spasm after treatment with botulinum toxin injections. Mov Disord 2006;21:73–78.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Cersósimo MG, Bertoti A, Roca CU, Micheli F. Botulinum toxin in a case of hemimasticatory spasm with severe worsening during pregnancy. Clin Neuropharmacol 2004;27:6–8.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Teive HA, Piovesan EJ, Germiniani FM, Camargo CH, Sa D, Scola RH, et al. Hemimasticatory spasm treated with botulinum toxin: case report. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2002;60:288–289.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Hemimasticatory spasm: a series of 17 cases and a comprehensive review of the literature
Kazuya Yoshida
Frontiers in Neurology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hemimasticatory spasm: possibilities of treatment with injections of botulinum neuroprotein type A (case report)
L. U. Valieva, A. S. Pankratov, O. R. Orlova
Neurology, Neuropsychiatry, Psychosomatics.2022; 14(3): 62. CrossRef - Bilateral Hemimasticatory spasm in a patient with hypereosinophilic syndrome
Kyung Ah Woo, Han-Joon Kim, Hyeyoung Park, Beomseok Jeon
Parkinsonism & Related Disorders.2021; 93: 55. CrossRef - Hemimasticatory spasm. Own experience of using botulinum neuroprotein type A
A. N. Korenko, A. V. Amelin, A. A. Timofeeva
The Scientific Notes of the Pavlov University.2021; 28(3): 47. CrossRef - Parry-Romberg Syndrome With Hemimasticatory Spasm: A Rare Combination
Guang-can Chen, Min-jie Chen, Wen-bin Wei, Yun-bo Hao
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2020; 31(2): e205. CrossRef - Hemi Masticatory Spasm: Series of 7 Cases and Review of Literature
Divya M. Radhakrishnan, Vinay Goyal, Garima Shukla, Mamta Bhushan Singh, M. Ramam
Movement Disorders Clinical Practice.2019; 6(4): 316. CrossRef
Comments on this article
 KMDS
KMDS
 E-submission
E-submission
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite