Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Mov Disord > Volume 15(1); 2022 > Article
-
Review Article
Evidence of Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease and Its Contribution to Synucleinopathy - Thuy Thi Lai1,2, Yun Joong Kim3, Hyeo-il Ma1,2, Young Eun Kim1,2
-
Journal of Movement Disorders 2022;15(1):1-14.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14802/jmd.21078
Published online: November 3, 2021
1Department of Neurology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea
2Hallym Neurological Institute, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea
3Department of Neurology, Yongin Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Yongin, Korea
- Corresponding author: Young Eun Kim, MD Department of Neurology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, 22 Gwanpyeong-ro 170beon-gil, Dongangu, Anyang 14068, Korea / Tel: +82-31-380-3740 / E-mail: yekneurology@hallym.or.kr
Copyright © 2022 The Korean Movement Disorder Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
- Accumulation of alpha-synuclein (αSyn) protein in neurons is a renowned pathological hallmark of Parkinson’s disease (PD). In addition, accumulating evidence indicates that activated inflammatory responses are involved in the pathogenesis of PD. Thus, achieving a better understanding of the interaction between inflammation and synucleinopathy in relation to the PD process will facilitate the development of promising disease-modifying therapies. In this review, the evidence of inflammation in PD is discussed, and human, animal, and laboratory studies relevant to the relationship between inflammation and αSyn are explored as well as new therapeutic targets associated with this relationship.
- The pathological hallmarks of Parkinson’s disease (PD), the second most common neurodegenerative disorder, include Lewy bodies, aggregated alpha-synuclein (αSyn) protein accumulation in neurons, and dopaminergic neuron degeneration. The pathology of αSyn-stained Lewy bodies has a spatial progression pattern associated with the disease course, which was proposed by Braak et al. [1]. Furthermore, mutations in the SNCA gene, which encodes the αSyn protein, especially copy number variation or aggregation-prone mutations, cause the familial form of PD [2-5]. Furthermore, misfolding and cell-to-cell transmission of αSyn protein have been evidenced using a fibrillar αSyn-injected animal model and by the emergence of Lewy body pathology in fetal nigral cells grafted into the striatum of PD patients [6-9]. Accordingly, the hypothesis that αSyn misfolding and propagation cause PD has become a popular theory by which to explain the pathophysiology of the disease.
- Various mechanisms, including autophagy–lysosomal pathway dysfunction or mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, are known to be involved in PD pathogenesis [10]. In addition, evidence that neuroinflammation is an important contributor to PD pathogenesis has emerged [11,12]. Epidemiological studies have found that various autoimmune diseases, such as type 1 diabetes, rheumatic disease, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis, are associated with an increased risk of PD development. Conversely, anti-inflammatory drugs, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids, can delay or prevent PD onset [13,14]. In a genome-wide association study, pleiotropy was observed between autoimmune disease and PD [15]. Moreover, in genetic studies, more than 90 loci of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) genes encoded by major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) have been identified. These genes participate in antigen presentation during the immune response and are associated with sporadic PD [16]. Thus, there is evidence that the immune response may be involved in the PD process. Although the precise role of inflammation in synucleinopathy is currently unclear, recent research demonstrates that inflammation is not only the result of the PD process but also an important contributor to the disease [11,12,17-19]. Therefore, the interaction between the immune response and synucleinopathy may be an important pathomechanism of PD and a possible target for future disease-modifying therapy.
- In this review, evidence of activated inflammation in PD is highlighted from autopsy data, in in vivo imaging, and laboratory findings. In addition, the temporal and molecular relationship between inflammation and synucleinopathy is evaluated in relation to various aspects of disease progression.
INTRODUCTION
- Epidemiological and genetic studies have demonstrated that inflammation may be associated with PD [15,16]. In addition, recent studies have reported that an altered gut microbiome in PD and its relevant gut inflammation may contribute to PD pathogenesis [20]. Evidence of inflammation in PD can be concretized by autopsy and in vivo studies. The immune response in the central nervous system (CNS) is distinct from that in the peripheral system in terms of the blood–brain barrier (BBB), resident glial cells (microglia and astrocytes), and absence of an adaptive immune response in itself [21]. However, because αSyn pathology in PD has been observed from the periphery, such as the enteric nervous system, to the central nervous system, immune responses should be evaluated inside and outside of the CNS in PD. This can be addressed by autopsy studies, in vivo imaging of inflammation, and laboratory analysis of the blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of patients (Table 1).
- An activated innate immune response was found in the postmortem PD brain
- Early studies demonstrated that innate immune cells were found in the postmortem PD brain. Both microglial and astrocytic activation was observed, with consistent microglial activation. Microglia constitute approximately 5%–12% of CNS cells and are capable of self-renewal independent of hematopoietic stem cells [22]. In the CNS, microglia present as major immune mediators; in particular, they perform the functions necessary for the recruitment of the immune system [22]. In PD postmortem studies, microglial activation was observed to varying degrees in different brain regions. Mirza et al. [23] described the activation of microglia labeled with CR3/43 and ferritin in the substantia nigra (SN) but not in the putamen of the PD brain. Moreover, MHC-II-expressing microglia are found at significantly higher levels in the SN, putamen, hippocampus, transentorhinal cortex, cingulate cortex, and temporal cortex as well as in the lymphatic system in PD than in the brain regions of normal controls [24]. Doorn et al. [25] showed differential microglial expression patterns in the PD brain and age-matched control brain: CD68-stained amoeboid microglia were identified in the SN and hippocampus, especially in the hippocampal CA2 region, whereas Iba1-stained microglia were significantly increased in the SN of the PD brain. However, such microglia were not found in the subregions of the hippocampus in age-matched control brains [25]. In another study, Kouli et al. [26] characterized microglial responses in various brain regions by human leukocyte antigen–DR isotype (HLA-DR) and Iba1 staining. They found significantly higher microglial activation in the amygdala of demented PD patients than in agematched controls [26]. Consequently, although microglia exhibited different activation patterns in terms of microglial phenotypic markers and PD brain regions, microglial activation was consistently observed in the postmortem PD brain.
- In addition to microglia, astrocytes are the most abundant CNS cell type. They demonstrate diverse morphological and functional characteristics dependent on specific brain areas [27]. Astrocytes are known to contribute to various physiological functions, including maintenance of neurons, formation of the BBB, and regulation of synapse functions [28]. Astrocytic activation in postmortem PD brains was thought not to exist because the differences in the distribution and cellular density of astrocytes stained for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) or metallothioneins I and II were not observed in the SN and putamen of PD patients [23]. However, astrocytes containing aggregated αSyn have been found in the PD brain, suggesting that astrocytes play a role in taking up abnormal αSyn [29,30]. Recently, reported data show that GFAP-positive astrocytes are significantly increased in the SN but are not found in other brain regions of PD subjects relative to age-matched controls [26]. Therefore, human autopsy studies demonstrate that microglial and astrocytic activation is involved in the PD process. However, the data obtained from postmortem brains might reflect the findings of advanced disease status or confounding terminal status affecting inflammation at death. Consequently, the in vivo status of PD must also be investigated.
- In vivo evidence of inflammation in PD patients
- In vivo evaluation can reflect the various stages of PD, and compared with autopsy data, it can better exclude the confounding factors affecting inflammation. Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging using ligands targeting microglial or astroglial activation has provided some insights into this respect.
- Activated microglia largely exist in two polarized states, namely, the M1 phenotype and the M2 phenotype [31]. The M1 phenotype is associated with the release of proinflammatory cytokines, whereas the M2 phenotype is accompanied by the production of anti-inflammatory molecules [31]. Current PET imaging using 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO), which is the main target for the development of ligands, can detect activated microglial status because this protein is expressed increasingly when microglia are activated. However, it is unclear why none of the current TSPO ligands are specific tracers of M1 or M2 microglia.
- Using 11C-PK11195 PET imaging, increased microglial activation was demonstrated in the pons, basal ganglia, frontal cortex, and temporal cortex in PD [32]. With the same ligand, microglial activation in the temporal and occipital regions of PD patients was demonstrated to be increased by 25%–30% compared with microglial activation in these regions in age-matched controls [33]. Increased microglial activation is also shown in the SN and putamen of patients with dementia with Lewy bodies (DLBs) as well as those with PD [34]. Similarly, compared with healthy controls, patients with idiopathic rapid-eye-movement sleep behavior disorder showed microglial activation in the SN [35]. These results indicate that microglia may be activated from the very early or preclinical stages of PD. In addition to 11C-PK11195 PET, microglial activation has been identified by other PET imaging ligands with improved binding qualities, such as 11C-DPA713, 18F-FEPPA, and 18F-DPA714 [36-38]. In a study using 11C-DPA713, a significant increase in uptake was shown in the occipital, temporal, and parietal cortex of the brains of PD patients [36]. Significantly higher microglial activation was also shown with 18F-DPA714 in the midbrain, frontal cortex, and putamen of PD patients relative to controls [38]. In summary, microglial activation has been evidenced in vivo by PET studies in the premotor or clinical stages of PD. It should be noted that different activation patterns occur in various brain regions as an effect of the ligand used, which is a limitation of such studies.
- From another perspective, increased astrocytic activation in the cortex and brain stem of early PD patients was identified using 11C-BU9908 PET imaging, which is a marker of the imidazoline 2 binding site and binds reactive astrocytes [39]. Therefore, in vivo PET imaging has provided further evidence of activated inflammation of innate immune cells in PD along with autopsy data.
- Activation of peripheral immune cells in PD
- In addition to the activation of innate CNS immune cells, peripheral lymphocyte infiltration has also been observed in the PD brain, which further demonstrates the immune association in PD [26,40-44]. Increased CD4 and CD8+ T cells but not B cells or natural killer (NK) cells have been observed in the SN of the postmortem PD brain [45]. In a recent study, CD4+ T cell infiltration was identified in postmortem brain sections, especially in the perivascular space and vessel wall directly in contact with astrocytes expressing MHC-II [41]. This suggested that astrocytes were capable of expressing the factors required for T cell infiltration and activation during PD progression [41]. In another study, a significant increase in CD4+ T lymphocytes in the SN was reported in demented PD patients, whereas a correlation existed between the number of CD4+ T cells and activated microglia in the amygdala [26]. In another study, a significant increase in CD8+ T cells but not CD4+ T cells was observed in the SN of PD patients compared with that in the SN of the control group, according to Lewy body staging [44]. The presence of infiltrating lymphocytes in specific brain regions affected by PD, such as the SN and amygdala, suggests that they reach these locations through targeted extravasation rather than through a random event.
- In addition, the peripheral blood of PD patients presents altered lymphocytic patterns [46-48]. Increased monocyte [46] or NK cell activation has also been reported in the blood of PD patients [47-50]. Furthermore, Niwa et al. [47] reported an increase in NK cells but not regulatory T cells and type 17 helper T cells in the blood of PD patients. Similarly, a significantly high percentage of NK cells with a lower percentage of CD3+ T cells and CD4+ T cells was identified in PD patients with clinical features relative to healthy controls [48].
- In addition to the blood, the CSF of PD patients has been shown to have higher activation of immune cells, such as T lymphocytes and monocytes, than that of control subjects [51]. Additional evidence of the increased number of monocytes in the CSF of PD patients was recently reported by Pillny et al. [52] These findings indicate that peripheral inflammatory cell activation occurs in the blood and CNS of PD patients and that peripheral immune cell activation may be involved in PD pathogenesis.
- However, it is less known how inflammation contributes to selective neuronal vulnerability in PD, but it is postulated that genetic predisposition combined with environmental factors may increase selective nigral dopaminergic degeneration during chronic inflammation [53].
- Changes in inflammatory mediators in PD
- In addition to the activation of innate CNS immune cells and peripheral immune cells, the levels of various inflammatory cytokines, which are produced by activated immune cells, have been investigated in PD [44,54-56]. The released cytokines may cause endogenous αSyn to misfold and aggregate. Aggregated αSyn can induce an inflammatory cell response that continues to release cytokines, which accounts for the continued presence of inflammation and progressive αSyn pathology [43].
- Altered cytokine expression has been detected in the postmortem PD brain [26,44,57]; cytokine expression was altered in the frontal cortex, with IL-2 levels significantly higher and IL-13 and IL-8 levels lower in PD brains than in controls [57]. In another study, a significant increase in the expression of proinflammatory IL-1β cytokine was observed in the SN and frontal cortex, whereas cytokine levels in other brain regions did not differ in PD patients and healthy controls [26].
- With regard to the inflammatory response in the peripheral system, Eidson et al. [55] found that the levels of two proinflammatory cytokines, namely, TNFα and IFNγ, were decreased in the serum of PD patients compared with that in the serum of control subjects. Recently, a significant increase in plasma proinflammatory cytokines, i.e., TNFα, IL-6, and IL-1β, was also found in PD patients [54,58,59]. However, variation in serum cytokine levels over the diurnal cycle must be cautiously interpreted, and various confounding factors, such as the diurnal cycle, drugs, and other medical conditions, must be controlled [55].
- The inflammasome is a cytoplasmic multiprotein complex that controls the inflammatory response and coordinates antimicrobial host defense, for which the essential components are a sensor protein, ASC adapter protein, and the inflammatory protease caspase-1. These components are assembled by the detection of pathogenic signals; inflammatory caspases are activated, and proinflammatory cytokines, i.e., IL-1β and IL-18, are released to induce cell death [60]. Inflammasome activation has been observed in the peripheral blood of PD patients. Expression of inflammasome NLRP3, a type of sensor protein, was found to be significantly increased in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of PD patients, whereas other types of inflammasomes (e.g., NLRP1 and NLRP4) did not differ between PD and control subjects [54]. Likewise, NLRP3 plasma levels were significantly higher in PD patients than in healthy controls in another study [56]. However, a recent study that used monocytes from peripheral blood did not find NLRP3 activation despite the detection of altered cytokine levels [61].
- Overall, the determination of cytokines or the inflammasome in synucleinopathy might provide new possible evidence of the association of inflammation and αSyn and could reveal potential biomarkers for PD.
EVIDENCE OF INFLAMMATION IN PD
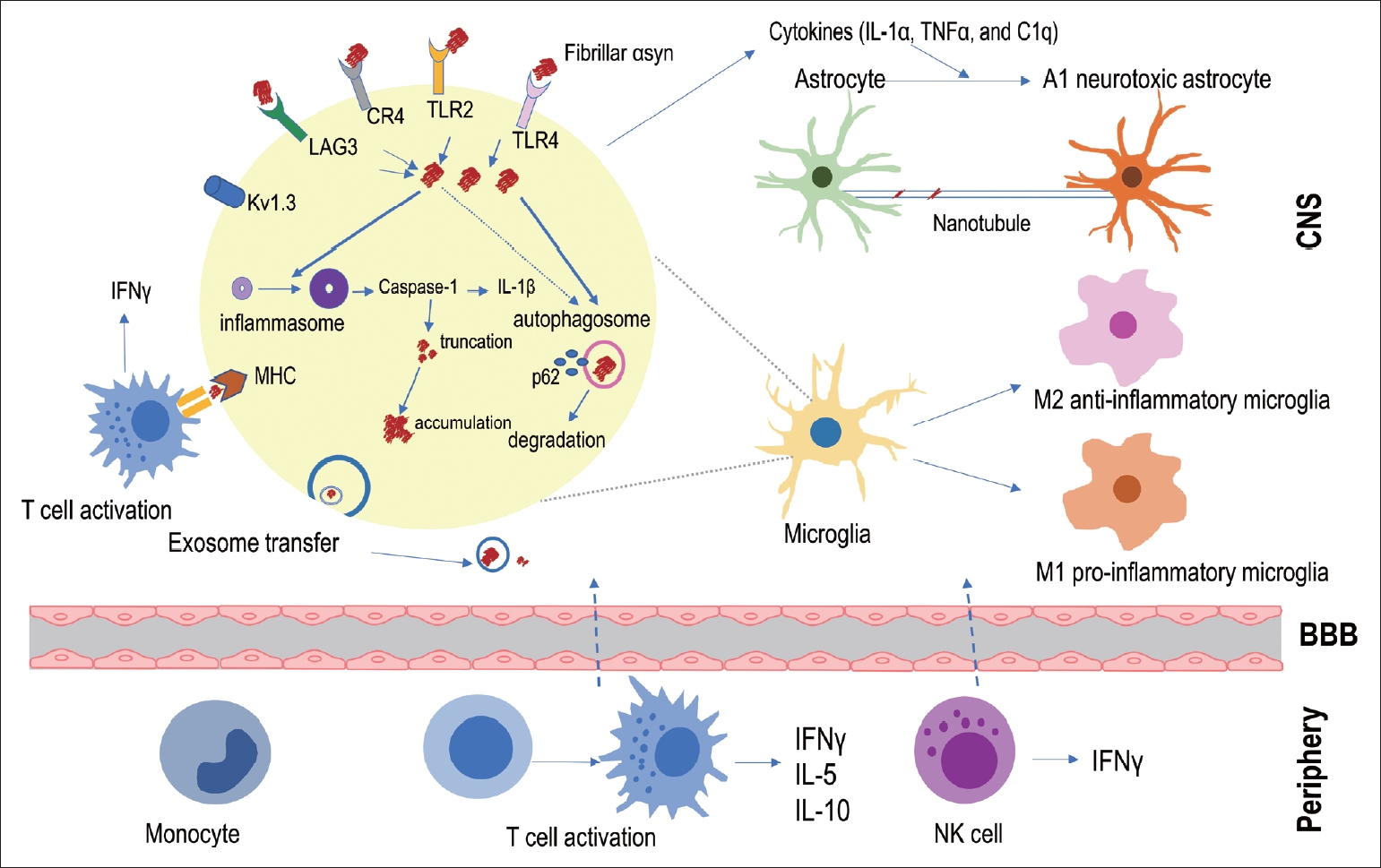
- Given the evidence of an activated inflammatory response from the postmortem PD brain, in in vivo PET imaging, and the CSF and blood of PD patients, a question arises: How does inflammation relate to αSyn propagation? Based on previous autopsy data, it was formerly postulated that inflammation might be the result of PD pathological progression. However, Olanow et al. [43] reported autopsy data from PD patients who received fetal nigral cell transplantation; infiltrating lymphocytes or macrophages and microglia were found around the transplanted cells from the beginning of grafting and even preceded αSyn accumulation inside the transplanted cells. In addition, Galiano-Landeira et al. [44] recently reported robust CD8+ T cell infiltration, especially in the earliest stage of Lewy body disease, in the comparative analysis of autopsy data from healthy controls, incidental Lewy body disease patients, and PD. A study investigating the relationship between T cell activity in PBMCs and the time of PD diagnosis in longitudinal observation demonstrated that αSyn-specific T cell reactivity was significantly increased in all periods of PD but was especially highest close to the onset of PD [42]. Overall, these findings indicate the possibility that inflammation can start from an early disease state and possibly precede αSyn pathology. Therefore, in this section of the review, the association between inflammation and αSyn pathological progression has been described in three parts: whether 1) αSyn triggers inflammation, 2) inflammation participates in αSyn removal, or 3) inflammation contributes to αSyn propagation (Figure 1).
- Pathological αSyn triggers inflammation
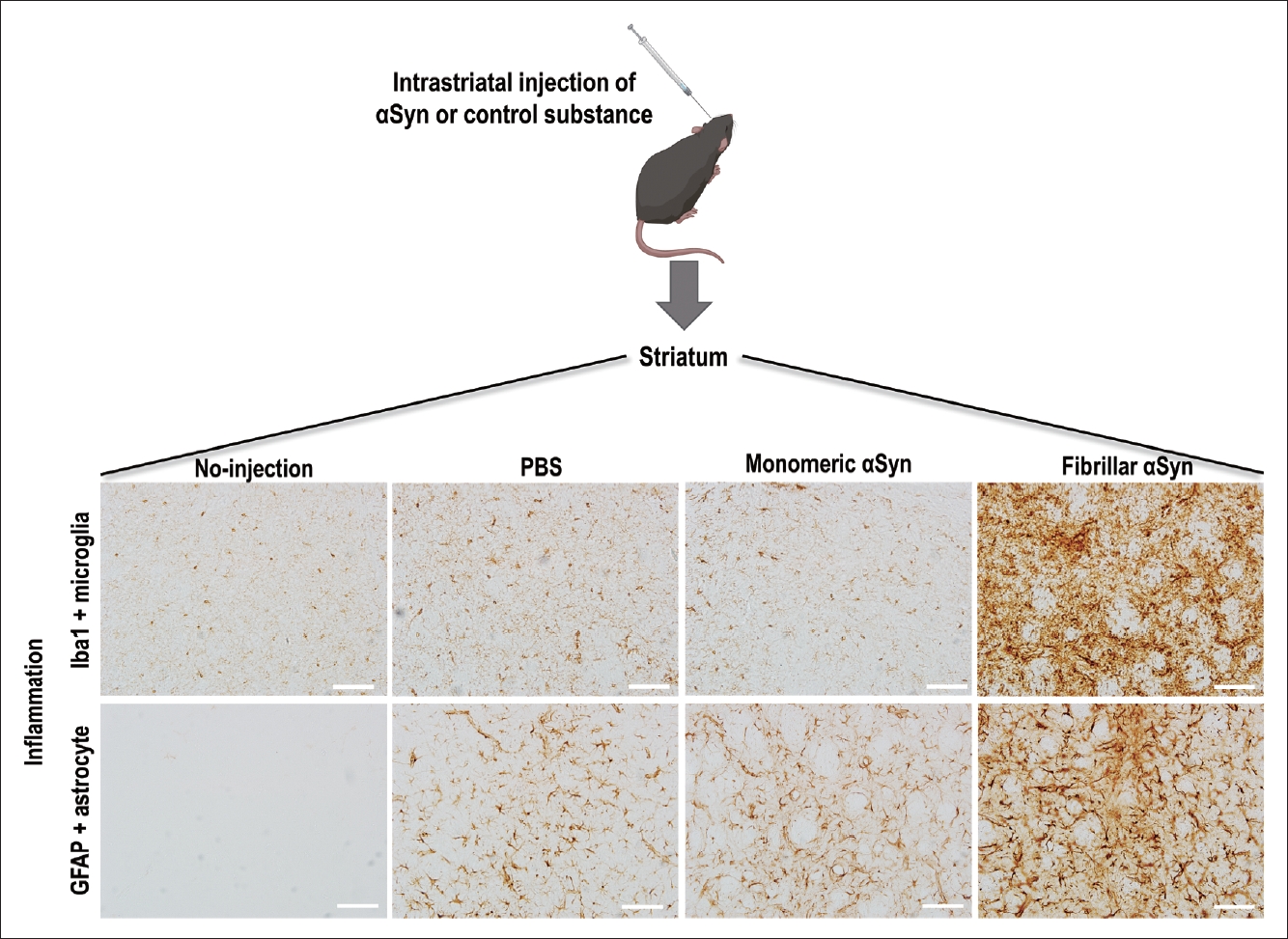
- PD animal models can provide evidence of immune cell activation during pathological αSyn introduction and its propagation [62-67]. After fibrillar αSyn injection into the brains of mice, thriving microglial and astrocytic activation was observed with αSyn propagation in these brains (Figure 2) [63,68,69]. Moreover, Lee et al. [70] reported that αSyn accumulation in glial cells produces proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. In addition, fibrillar αSyn has been shown to induce an inflammatory response through synthesis of IL-1β through toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 interactions, which thereby leads to the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, followed by increased reactive oxygen species production in human monocytes [71]. This suggests that fibrillar αSyn encounters the TLR2 receptor on the surface of immune cells and triggers a downstream signaling pathway with the subsequent production of cytokines and inflammatory molecules. The roles of TLR4 and TLR2 in relation to pathological αSyn have been identified in several studies [72-75]. The involvement of other immune receptors in pathological αSyn has also been reported, e.g., cellsurface lymphocyte activation gene 3 protein (LAG3) [76,77] and complement receptor 4 (CR4) [78], indicating that αSyn triggers an inflammatory response through interactions with various immune receptor-mediated pathways. A recent study identified the upregulation of microglial voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 in response to aggregated αSyn in primary microglial cultures [79].
- In a recent study by Li et al. [80], the authors investigated microglial phenotypic polarization against αSyn and found that monomeric αSyn modulated microglia toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype after exposure, whereas oligomeric αSyn led microglia toward a proinflammatory phenotype. This suggests that the pathologic form of αSyn may contribute to the aggravation of inflammation, unlike monomeric αSyn.
- In addition to the inflammatory response through glial cells, the adaptive immune response through lymphocytes may be affected by αSyn. Following fibrillar αSyn injection into the CNS parenchyma, a significant increase in peripheral immune cell infiltration, such as B lymphocyte (CD19+), T helper lymphocyte (CD4+), T cytotoxic lymphocyte (CD8+), activated myeloid cell (CD11+), and NK cell infiltration, was observed in the CNS compared with the effects in a monomer-injected mouse model [63]. Likewise, an alteration of peripheral immune cells was identified in the blood and peripheral organs, including the spleen and lymph nodes, following fibrillar αSyn injection into the brain [63]. These data suggest that pathological αSyn triggers immune cell infiltration and activation in the brain as well as in the peripheral system. Moreover, Harms et al. [81] reported that αSyn overexpression induced MHC-II-mediated antigen presentation on microglia to CD4+ T cell expression; thus, the interaction between microglia and CD4+ T cells led to potent cytokine production. In agreement with this, a recent study demonstrated that αSyn triggers incremental MHC-II expression associated with an accompanying T cell response; therapeutic targeting of T cell disruption in animal models was found to reduce MHC-II expression as well as CNS myeloid cells in relation to αSyn expression [82].
- To understand the differential contribution of various peripheral immune cells in synucleinopathy, Iba et al. [83] evaluated T lymphocyte populations in 10–11-month-old transgenic mice overexpressing human αSyn, which demonstrated considerable accumulation of αSyn in the cortical and subcortical regions. The authors found an increase in the number of CD3 and CD4+ T cells in mouse brains, and CD3+ T cells were detected in close proximity to glial cells (Iba1 and GFAP) and human αSyn (SYN211)-positive neurons in the neocortex, hippocampus, and striatum, which supports previous observations in the human brain [40,41]. Furthermore, an accompanying increase in IFNγ and CD1d-restricted NK T cells was identified in this animal model [83]. In another study, when αSyn oligomer was increased using an injection of adeno-associated virus coding αSyn in the T cell-competent rat brain, the presence of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell infiltration was correlated with the upregulation of MHC-II-expressing microglia. However, this correlation was not observed in T cell-deficient rats [69]. Taken together, these studies imply that pathological αSyn contributes to the recruitment of lymphocytes as well as the activation of innate immune cells.
- Inflammation opposes αSyn toxicity
- One of the primary roles of microglia and astrocytes is their macrophage-like function [84,85]. Lee et al. [86] explored the efficiency of clearing extracellular αSyn in different brain cell types, including neurons, astrocytes, and microglia, and found that microglia exhibited the highest rate of αSyn clearance. Supporting evidence by Loria et al. [87] also indicated that astrocytes were able to efficiently clear fibrillar αSyn more efficiently than neurons. A recent study by Tsunemi et al. [88] also emphasized the importance of lysosomal function in astrocytes for αSyn degradation during the pathogenesis of the disease. Although neurons and astrocytes can clear αSyn, microglia are the major immune cells that quickly engulf and degrade αSyn to maintain brain health by changing their morphological state to M1 (the proinflammatory phenotype) or M2 (the antiinflammatory phenotype) [89]. Choi et al. [74] suggested that the neuroprotective function of microglia occurs through ingestion and degradation of neuron-released αSyn through a selective autophagy mechanism. Therefore, a better understanding of microglial function in relation to αSyn will likely contribute to the identification of therapeutic targets for inflammation in synucleinopathies.
- In studies of the cellular mechanism underlying αSyn clearance, in vitro research has identified that αSyn alters microglial function through interactions with TLR [72,73,75,90]. Stefanova et al. [72] demonstrated that TLR4 deficiency in αSyn-overexpressing transgenic mice led to significantly increased levels of αSyn in the midbrain and forebrain compared with αSyn-overexpressing transgenic mice with intact TLR4 expression, indicating that impairment of TLR4 influences extracellular αSyn clearance through microglia. In accordance with this study, Fellner et al. [73] indicated that TLR4 is required for the αSyn-dependent activation of glial cells. In addition, TLR4 was recently linked to selective autophagic degradation of αSyn in synucleinopathy [74], whereas oligomeric αSyn interacts with TLR2 to induce microglial activation [90]. Therefore, the modulation of the TLR response to αSyn can be a possible treatment target for the improvement of αSyn propagation.
- Disruption of the BBB in synucleinopathy has been observed in a PD animal model [91]; this process may allow the entrance of peripheral immune cells into the brain for pathological αSyn clearance. A recent study demonstrated the protective role of NK cells (granular lymphocytes of the innate immune system) in efficiently internalizing and degrading extracellular αSyn; the systemic depletion of NK cells in a PD mouse model exacerbated motor abnormalities and αSyn propagation compared with the effects in a control group [92]. In another study, reconstitution of T cell populations reduced αSyn accumulation and resulted in persistent microgliosis in the striatum of mice with an immune system impaired by αSyn preformed fibril injection [93]. These data support that NK cells, T lymphocytes, microglia, and astrocytes can play protective roles in the αSyn pathology of PD.
- Inflammation contributes to αSyn propagation
- Accumulating evidence now supports the case that glial activation contributes to αSyn propagation. Microglial exosomes also contribute to the progression of αSyn pathology through exosomal transfer of αSyn from cell to cell [17,19]. In addition, reactive microglia enhance the transmission of exosomal αSyn through TLR2 [94]. Recently, Izco et al. [95] investigated the temporal relationship between αSyn and inflammation in a mouse model of PD. They found that the peak expression of Iba1-positive microglia, GFAP-positive astrocytes, and IL-1β occurred before αSyn accumulation [95]. Furthermore, several researchers have been able to block or suppress microglial activation using pharmacological drugs and thereby have identified decreases in αSyn pathology in a mouse model [17,94].
- There is also evidence that astrocytes actively transfer aggregated αSyn to healthy astrocytes through direct contact or tunneling nanotubes [41,96]. Ngolab et al. [97] demonstrated that DLB brain-derived exosomes trigger αSyn accumulation in astrocytes in the mouse brain, suggesting the participation of astrocytes in αSyn transmission. In addition, activated microglia have been shown to induce neurotoxic A1 astrocytes by secreting IL-1α, TNFα, and C1q complements [98]. Thus, Yun et al. [99] demonstrated that microglia-induced inhibition of A1 astrocytes led to a decrease in pathological αSyn in an animal model.
- A recent study using intranasal infusion of endotoxin–lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to induce olfactory bulb (OB) inflammation in mice found that LPS triggered microglial activation, inflammatory cytokine expression, and phosphorylated αSyn accumulation in the OB and SN through IL-1β/IL-1 receptor 1-dependent signaling [100]. This finding suggests that inflammation, particularly IL-1, plays a role in mediating the initiation and propagation of αSyn pathology from the OB [100].
- In relation to systemic inflammation, La Vitola et al. [101] developed a PD mouse model through systemic administration of LPS followed by intracerebroventricular injection of an αSyn oligomer as well as an αSyn-overexpression transgenic mouse administered LPS. The authors demonstrated that peripherally induced neuroinflammation influences the action of αSyn oligomers to potentiate a detrimental effect [101]. The influence of the adaptive immune system on αSyn has also been explored [102]. By crossing human αSyn-overexpressing transgenic mice and lymphocytelacking mice, Sommer et al. [102] determined that the presence of T lymphocytes modulated toward a proinflammatory M1 phenotype was associated with an increased number of αSyn aggregates in the SN and striatum. Their findings indicate that the inflammatory response contributes to αSyn transmission through various pathways.
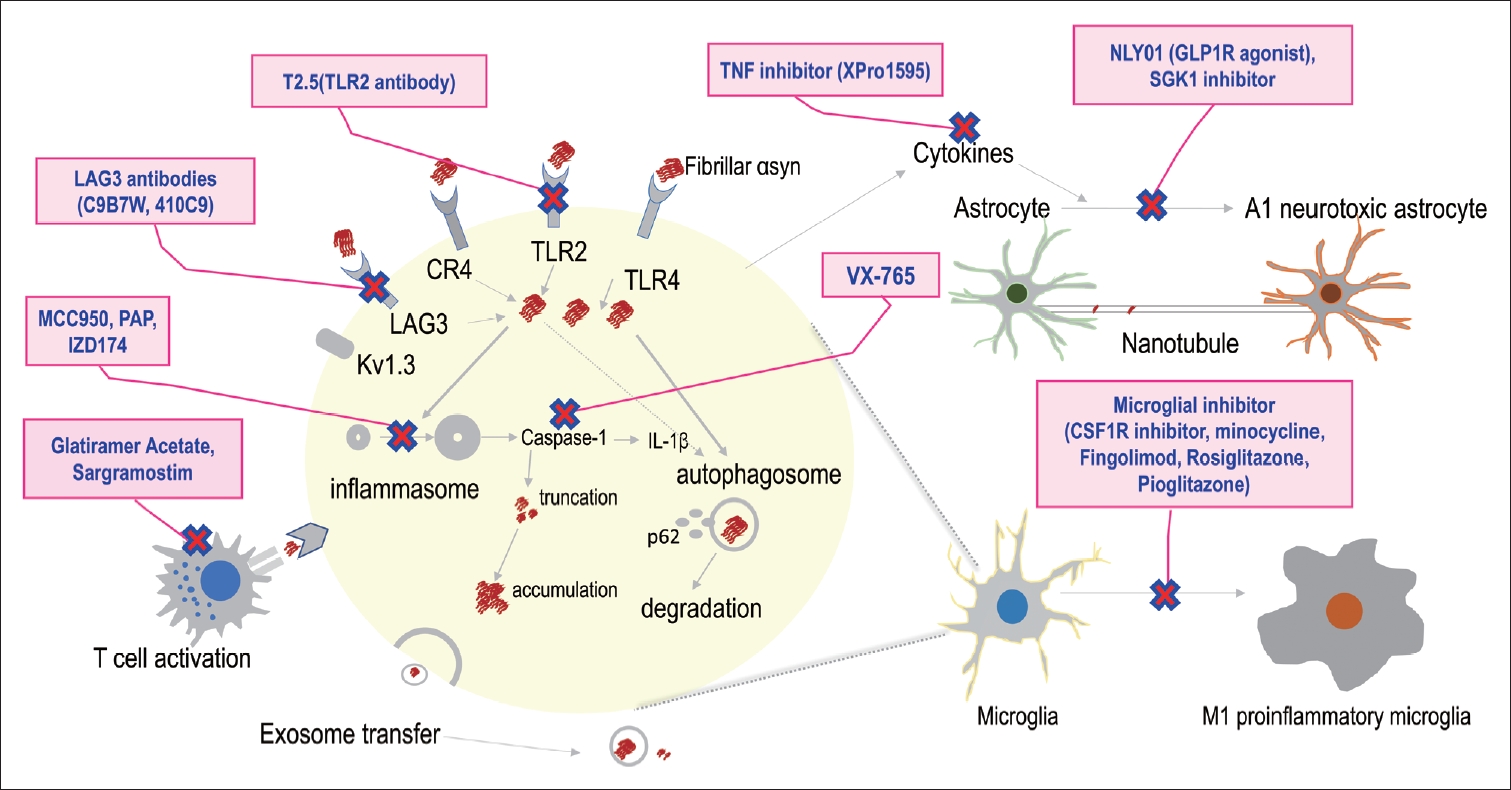
- Therapeutic strategies targeting the interaction between inflammation and αSyn in PD
- As discussed above, extensive evidence suggests that inflammation plays a critical role in αSyn-associated PD pathogenesis (Figure 1). Therefore, researchers have explored treatment targets by modulating the immune response to ameliorate αSynassociated PD pathology (Figure 3). This has led to numerous preclinical and clinical trials, as presented in Table 2 [103-117].
THE ASSOCIATION OF INFLAMMATION AND SYNUCLEINOPATHY
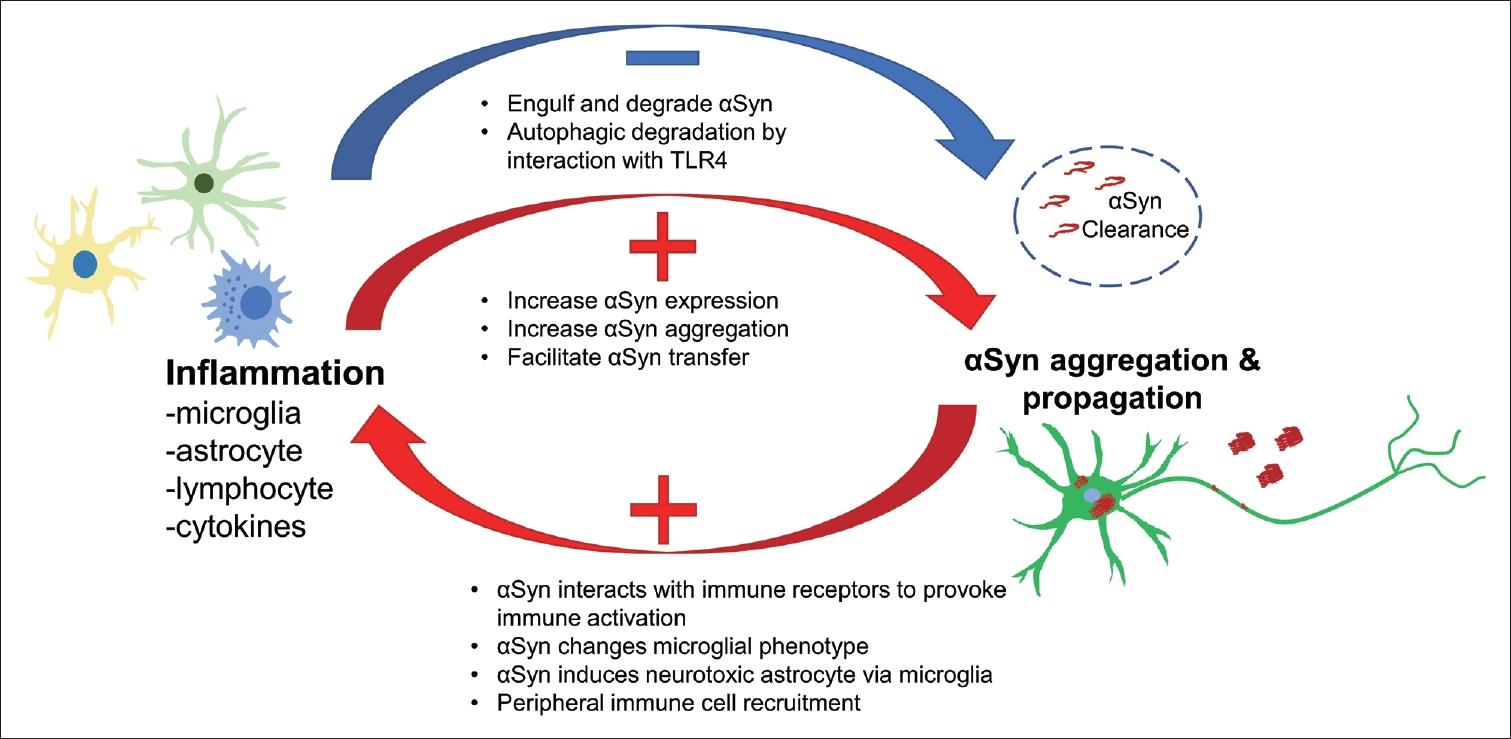
- In conclusion, inflammation plays important roles in αSyn-related pathological processes and vice versa. Based on the current understanding, CNS innate immune cells, i.e., microglia and astrocytes, are activated in response to pathological αSyn, promote the propagation of αSyn, and clear abnormal αSyn. In addition, peripheral immune cells, such as lymphocytes and NK cells, interact with CNS innate immune cells responding to abnormal αSyn and contribute to αSyn propagation (Figure 4). A vicious cycle is thereby created through the interaction between activated inflammation and αSyn propagation, which may support prolonged PD progression. Thus, blocking this cycle using anti-inflammatory methods could represent a promising option for future therapy.
CONCLUSION
-
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
-
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the Hallym University Research Fund and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean Government (MSIT) (2020R1F1076697).
-
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Young Eun Kim. Data curation: Thuy Thi Lai, Young Eun Kim. Investigation: Thuy Thi Lai, Young Eun Kim. Methodology: Thuy Thi Lai, Young Eun Kim. Supervison: Yun Joong Kim, Hyeo-il Ma. Writing—original draft: Thuy Thi Lai, Young Eun Kim. Writing—reviewing: all authors.
Notes
| Type of inflammation | Markers for inflammation | Sources | Regions | PD vs. healthy control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microglia | Iba1 | Postmortem brain | SN | Increase [25] |
| SN, HIP, ERC, PFC, OTC, PPC, Mesencephalon | No difference [25], [26], [41] | |||
| HLA-DR | Amygdala | Increase [26] | ||
| SN | No difference [26] | |||
| CR3/43 | SN | Increase [23] | ||
| Putamen | No difference [23] | |||
| CD68 | SN, HIP | Increase [25] | ||
| TMEM119 | Putamen | Increase [43] | ||
| 11C-PK11195 | PET imaging | Temporal cortex, occipital cortex, SN, putamen | Increase [33]- [35] | |
| Putamen, caudate nucleus | No difference [35] | |||
| 11C-DPA713 | Temporal cortex, occipital cortex, parietal cortex | Increase [38] | ||
| 18F-FEPPA | Thalamus, caudate, putamen, HIP | Increase [37] | ||
| 18F-DPA714 | Midbrain, frontal cortex, putamen | Increase [38] | ||
| Astrocyte | GFAP | Postmortem brain | SN | Increase [26] |
| Amygdala, HIP, ERC, PFC, OTC, PPC, Mesencephalon | No difference [41], [83] | |||
| GLAST | Mesencephalon | No difference [41] | ||
| Metallothioneins I and II | SN, putamen | No difference [23] | ||
| MHC-II | SN, putamen, HIP, transentorhinal cortex, cingulate cortex, temporal cortex, lymphatic system, mesencephalon | Increase [24], [41] | ||
| 11C-BU9908 | PET imaging | Cortex, brain stem | Increase [39] | |
| Lymphocyte | CD4+ | Postmortem brain | SN, amygdala | Increase [26], [41], [45] |
| Blood | PBMC | Increase [42] | ||
| Peripheral blood lymphocytes | Lower [48] | |||
| CD8+ | Postmortem brain | SN | Increase [44] | |
| SN, perivascular, amygdala | No difference [26], [44], [45] | |||
| Blood | PBMC | No difference [42] | ||
| CD45 | Postmortem brain | Putamen | Increase [43] | |
| B cells | CD79α+ | Postmortem brain | SN | No difference [45] |
| CD20+ | ||||
| NK cells | CD57+ | Postmortem brain | SN | No difference [45] |
| CD56+ | Blood | PBMC | Increase [47], [48], [50] | |
| Monocytes | CD14+ | Blood | Peripheral blood | Increase [46] |
| CD16+ | Peripheral blood | No difference [51] | ||
| CD14+/CD16- | CSF | CSF | Lower [51] | |
| CD14+/CD16+ | CSF | Increase [51] | ||
| Inflammasome | NLRP3 | Blood | PBMC, plasma | Increase [54], [56] |
| PBMC | No difference [61] | |||
| NLRP1 | PBMC | No difference [54] | ||
| NLRP4 | ||||
| Cytokines | IL-1β | Postmortem brain | SN, frontal cortex | Increase [26] |
| Blood | Plasma, serum | Increase [103] | ||
| IFNγ | Blood | PBMC | No difference [42] | |
| Serum | Lower [55] | |||
| TNFα | Postmortem brain | SN, HIP, amygdala, frontal cortex | No difference [26] | |
| Blood | Serum | Lower [55] | ||
| Plasma | Increase [58] | |||
| IL-2 | Postmortem brain | Frontal cortex | Increase [57] | |
| IL-13 | Frontal cortex | Lower [57] | ||
| IL-10 | Blood | PBMC, plasma | Increase [42], [58] | |
| IL-5 | PBMC | No difference [42] | ||
| IL-6 | Blood | Plasma | Increase [58] |
PD, Parkinson’s disease; SN, substantia nigra; HIP, hippocampus; ERC, entorhinal cortex; PFC, prefrontal cortex; OTC, occipito-temporal cortex; PPC, posterior pariental cortex; HLA-DR, human leukocyte antigen DR isotype; PET, positron emission tomography; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; GLAST, glutamate aspartate transporter; MHC-II, major histocompatibility complex class II; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; NK cells, natural killer cells; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid.
| Category | Compound | Description | Findings | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microglia | CSF1R inhibitor (PPLX3397-Pexidartinib) | Inhibits microglia/macrophage | Depletion of microglia suppressed αSyn aggregation and transmission in mice [17, 94] | Preclinical |
| Minocycline (Mino) | Reduces the proliferation/activation of resting microglia | Prevention of the dopaminergic neurons loss, increased the dopamine level, decreased the Lewy body pathology in mice [104] | Phase 2 | |
| NINDS NET-PD | ||||
| Fingolimod | Blocks T cell egress from lymph nodes (prevents T-cell entry to the brain) | Decreased αSyn pathology in enteric nervous system of A53T transgenic mice [105] | Preclinical | |
| Rosiglitazone | PPARγ, inhibits microglial release of TNFα | Reduced αSyn pathology and prevented loss of dopaminergic neurons [106] | Preclinical | |
| Pioglitazone | PPARγ agonists, inhibits microglia activation | Modifies progression in early PD [107] | Phase 2 | |
| Astrocyte | NLY01 (GLP-1R agonist) | Blocks A1 neurotoxic astrocyte generation by microglia | Reduced αSyn pathology in A53T transgenic mice [99] | Preclinical |
| Phase 1, the drug was found to be safe and well-tolerated | Phase 2 | |||
| NCT03672604 | ||||
| SGK1 inhibitor | SGK1 is negatively regulated by Nurr and Fox2 in glial cells | Ameliorated neuronal αSyn aggregation and protected dopaminergic neuron loss [108] | Preclinical | |
| TLR2 | T2.5 antibodies | Blocks TLR2 | Decreased αSyn pathology and inflammation in mice [109] | Preclinical |
| LAG3 receptor | LAG3 antibodies (C9B7W and 410C9) | Blocks LAG3 receptor | Reduced αSyn transmission [77] | Preclinical |
| T lymphocytes | GA | Attenuates the activation of CD4+T cells and the pro-inflammatory response | Improved the motor function and restored the αSyn level in the midbrain and striatum of MPTP-treated mice [110] | Preclinical |
| Sargramostim (Leukine) | Human recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor affects myeloid recovery | Sargramostim treatment in PD is well-tolerated [111] | Phase 1 | |
| NCT010882010 | ||||
| Inflammasome | MCC950 | Blocks ATP and nigericin dependent NLRP3 activation | Prevented inflammasome activation by fibrillar αSyn, and led to less neuron loss and better dopaminergic signaling [112] | Preclinical |
| PAP | Selective inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 10A activity | Inhibited αSyn aggregation and neuronal cell death results from MPTP/P mice model [113] | Preclinical | |
| VX-765 (caspase-1 inhibitor) | Inhibits proteolytic processing of IL-1β and IL-18 to secreted forms | Inhibition of caspase-1 rescued BE(2)-M17 human dopaminergic neuroblastoma cells from the toxic effects of αSyn [114] | Preclinical | |
| Reduced αSyn pathology in transgenic mouse model of MSA [115] | ||||
| Inzomelid (IZD174) (NLRP3 inhibitor) | Inhibitor of inflammasomes containing NLRP3, or nod-like receptor family, pyrin domain-containing protein 3 | The treatment was well tolerated in double-blind evaluations in healthy volunteers | Phase 1 | |
| NCT04338997 | ||||
| Cytokines | XPro1595 (TNF inhibitor) | Targeted soluble TNF | Reduced the αSyn protein level [116] | Preclinical |
| Neuroprotective effects in rat model [117] |
αSyn, alpha-synuclein; PD, Parkinson’s disease; NINDS NET-PD, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke Neuroprotection Exploratory Trials in Parkinson’s Disease; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma; GLP-1R, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; SGK1, serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 inhibitor; TLR, toll-like receptor; GA, glatiramer acetate; MPTP, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; PAP, papaverine; IL, interleukin; MSA, multiple system atrophy; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
- 1. Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2003;24:197–211.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Giasson BI, Uryu K, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM. Mutant and wild type human α-synucleins assemble into elongated filaments with distinct morphologies in vitro. J Biol Chem 1999;274:7619–7622.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Flagmeier P, Meisl G, Vendruscolo M, Knowles TP, Dobson CM, Buell AK, et al. Mutations associated with familial Parkinson’s disease alter the initiation and amplification steps of α-synuclein aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016;113:10328–10333.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, Singleton A, Hague S, Kachergus J, et al. α-synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 2003;302:841.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Chartier-Harlin MC, Kachergus J, Roumier C, Mouroux V, Douay X, Lincoln S, et al. α-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2004;364:1167–1169.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Kordower JH, Chu Y, Hauser RA, Freeman TB, Olanow CW. Lewy body-like pathology in long-term embryonic nigral transplants in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Med 2008;14:504–506.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Li JY, Englund E, Holton JL, Soulet D, Hagell P, Lees AJ, et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in subjects with Parkinson’s disease suggest host-to-graft disease propagation. Nat Med 2008;14:501–503.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Luk KC, Kehm V, Carroll J, Zhang B, O’Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, et al. Pathological α-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science 2012;338:949–953.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Shin J, Kim HJ, Jeon B. Immunotherapy targeting neurodegenerative proteinopathies: α-synucleinopathies and tauopathies. J Mov Disord 2020;13:11–19.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Zhang J, Culp ML, Craver JG, Darley-Usmar V. Mitochondrial function and autophagy: integrating proteotoxic, redox, and metabolic stress in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 2018;144:691–709.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Brás IC, Dominguez-Meijide A, Gerhardt E, Koss D, Lázaro DF, Santos PI, et al. Synucleinopathies: where we are and where we need to go. J Neurochem 2020;153:433–454.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Hirsch EC, Standaert DG. Ten unsolved questions about neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 2021;36:16–24.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Chen H, Zhang SM, Hernán MA, Schwarzschild MA, Willett WC, Colditz GA, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the risk of Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 2003;60:1059–1064.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Fyfe I. Aspirin and ibuprofen could lower risk of LRRK2 Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol 2020;16:460.Article
- 15. Witoelar A, Jansen IE, Wang Y, Desikan RS, Gibbs JR, Blauwendraat C, et al. Genome-wide pleiotropy between Parkinson disease and autoimmune diseases. JAMA Neurol 2017;74:780–792.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Tan EK, Chao YX, West A, Chan LL, Poewe W, Jankovic J. Parkinson disease and the immune system - associations, mechanisms and therapeutics. Nat Rev Neurol 2020;16:303–318.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Guo M, Wang J, Zhao Y, Feng Y, Han S, Dong Q, et al. Microglial exosomes facilitate α-synuclein transmission in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2020;143:1476–1497.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18. Harms AS, Kordower JH, Sette A, Lindestam Arlehamn CS, Sulzer D, Mach RH. Inflammation in experimental models of α-synucleinopathies. Mov Disord 2021;36:37–49.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Xia Y, Zhang G, Han C, Ma K, Guo X, Wan F, et al. Microglia as modulators of exosomal alpha-synuclein transmission. Cell Death Dis 2019;10:174.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Lin CH, Chen CC, Chiang HL, Liou JM, Chang CM, Lu TP, et al. Altered gut microbiota and inflammatory cytokine responses in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 2019;16:129.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Ousman SS, Kubes P. Immune surveillance in the central nervous system. Nat Neurosci 2012;15:1096–1101.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Hickman S, Izzy S, Sen P, Morsett L, El Khoury J. Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci 2018;21:1359–1369.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Mirza B, Hadberg H, Thomsen P, Moos T. The absence of reactive astrocytosis is indicative of a unique inflammatory process in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 1999;95:425–432.Article
- 24. Imamura K, Hishikawa N, Sawada M, Nagatsu T, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y. Distribution of major histocompatibility complex class II-positive microglia and cytokine profile of Parkinson’s disease brains. Acta Neuropathol 2003;106:518–526.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Doorn KJ, Moors T, Drukarch B, van de Berg WDj, Lucassen PJ, van Dam AM. Microglial phenotypes and toll-like receptor 2 in the substantia nigra and hippocampus of incidental Lewy body disease cases and Parkinson’s disease patients. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2014;2:90.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Kouli A, Camacho M, Allinson K, Williams-Gray CH. Neuroinflammation and protein pathology in Parkinson’s disease dementia. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2020;8:211.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 27. Khakh BS, Sofroniew MV. Diversity of astrocyte functions and phenotypes in neural circuits. Nat Neurosci 2015;18:942–952.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 28. Siracusa R, Fusco R, Cuzzocrea S. Astrocytes: role and functions in brain pathologies. Front Pharmacol 2019;10:1114.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Braak H, Sastre M, Del Tredici K. Development of α-synuclein immunoreactive astrocytes in the forebrain parallels stages of intraneuronal pathology in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 2007;114:231–241.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Sorrentino ZA, Giasson BI, Chakrabarty P. α-synuclein and astrocytes: tracing the pathways from homeostasis to neurodegeneration in Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol 2019;138:1–21.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Shen Z, Bao X, Wang R. Clinical PET imaging of microglial activation: implications for microglial therapeutics in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 2018;10:314.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Gerhard A, Pavese N, Hotton G, Turkheimer F, Es M, Hammers A, et al. In vivo imaging of microglial activation with [11C](R)-PK11195 PET in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 2006;21:404–412.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Edison P, Ahmed I, Fan Z, Hinz R, Gelosa G, Ray Chaudhuri K, et al. Microglia, amyloid, and glucose metabolism in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013;38:938–949.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Iannaccone S, Cerami C, Alessio M, Garibotto V, Panzacchi A, Olivieri S, et al. In vivo microglia activation in very early dementia with Lewy bodies, comparison with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2013;19:47–52.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Stokholm MG, Iranzo A, Østergaard K, Serradell M, Otto M, Svendsen KB, et al. Assessment of neuroinflammation in patients with idiopathic rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder: a case-control study. Lancet Neurol 2017;16:789–796.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Terada T, Yokokura M, Yoshikawa E, Futatsubashi M, Kono S, Konishi T, et al. Extrastriatal spreading of microglial activation in Parkinson’s disease: a positron emission tomography study. Ann Nucl Med 2016;30:579–587.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Ghadery C, Koshimori Y, Coakeley S, Harris M, Rusjan P, Kim J, et al. Microglial activation in Parkinson’s disease using [18F]-FEPPA. J Neuroinflammation 2017;14:8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Lavisse S, Goutal S, Wimberley C, Tonietto M, Bottlaender M, Gervais P, et al. Increased microglial activation in patients with Parkinson disease using [18F]-DPA714 TSPO PET imaging. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2021;82:29–36.ArticlePubMed
- 39. Wilson H, Dervenoulas G, Pagano G, Tyacke RJ, Polychronis S, Myers J, et al. Imidazoline 2 binding sites reflecting astroglia pathology in Parkinson’s disease: an in vivo 11C-BU99008 PET study. Brain 2019;142:3116–3128.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Chan L, Chung CC, Chen JH, Yu RC, Hong CT. Cytokine profile in plasma extracellular vesicles of Parkinson’s disease and the association with cognitive function. Cells 2021;10:604.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 41. Rostami J, Fotaki G, Sirois J, Mzezewa R, Bergström J, Essand M, et al. Astrocytes have the capacity to act as antigen-presenting cells in the Parkinson’s disease brain. J Neuroinflammation 2020;17:119.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 42. Lindestam Arlehamn CS, Dhanwani R, Pham J, Kuan R, Frazier A, Rezende Dutra J, et al. α-synuclein-specific T cell reactivity is associated with preclinical and early Parkinson’s disease. Nat Commun 2020;11:1875.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 43. Olanow CW, Savolainen M, Chu Y, Halliday GM, Kordower JH. Temporal evolution of microglia and α-synuclein accumulation following foetal grafting in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2019;142:1690–1700.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Galiano-Landeira J, Torra A, Vila M, Bové J. CD8 T cell nigral infiltration precedes synucleinopathy in early stages of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2020;143:3717–3733.ArticlePubMed
- 45. Brochard V, Combadière B, Prigent A, Laouar Y, Perrin A, Beray-Berthat V, et al. Infiltration of CD4+ lymphocytes into the brain contributes to neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson disease. J Clin Invest 2009;119:182–192.ArticlePubMed
- 46. Wijeyekoon RS, Kronenberg-Versteeg D, Scott KM, Hayat S, Jones JL, Clatworthy MR, et al. Monocyte function in Parkinson’s disease and the impact of autologous serum on phagocytosis. Front Neurol 2018;9:870.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 47. Niwa F, Kuriyama N, Nakagawa M, Imanishi J. Effects of peripheral lymphocyte subpopulations and the clinical correlation with Parkinson’s disease. Geriatr Gerontol Int 2012;12:102–107.ArticlePubMed
- 48. Sun C, Zhao Z, Yu W, Mo M, Song C, Si Y, et al. Abnormal subpopulations of peripheral blood lymphocytes are involved in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Transl Med 2019;7:637.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 49. Earls RH, Lee JK. The role of natural killer cells in Parkinson’s disease. Exp Mol Med 2020;52:1517–1525.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 50. Mihara T, Nakashima M, Kuroiwa A, Akitake Y, Ono K, Hosokawa M, et al. Natural killer cells of Parkinson’s disease patients are set up for activation: a possible role for innate immunity in the pathogenesis of this disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2008;14:46–51.ArticlePubMed
- 51. Schröder JB, Pawlowski M, Meyer Zu Hörste G, Gross CC, Wiendl H, Meuth SG, et al. Immune cell activation in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurol 2018;9:1081.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 52. Pillny C, Nitsch L, Proske-Schmitz S, Sharma A, Wüllner U. Abnormal subpopulations of monocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2021;84:144–145.ArticlePubMed
- 53. Tansey MG, Goldberg MS. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: its role in neuronal death and implications for therapeutic intervention. Neurobiol Dis 2010;37:510–518.ArticlePubMed
- 54. Fan Z, Pan YT, Zhang ZY, Yang H, Yu SY, Zheng Y, et al. Systemic activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and plasma α-synuclein levels are correlated with motor severity and progression in Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 2020;17:11.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 55. Eidson LN, Kannarkat GT, Barnum CJ, Chang J, Chung J, Caspell-Garcia C, et al. Candidate inflammatory biomarkers display unique relationships with alpha-synuclein and correlate with measures of disease severity in subjects with Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 2017;14:164.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 56. Chatterjee K, Roy A, Banerjee R, Choudhury S, Mondal B, Halder S, et al. Inflammasome and α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: a cross-sectional study. J Neuroimmunol 2020;338:577089.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Rydbirk R, Elfving B, Andersen MD, Langbøl MA, Folke J, Winge K, et al. Cytokine profiling in the prefrontal cortex of Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy patients. Neurobiol Dis 2017;106:269–278.ArticlePubMed
- 58. Usenko TS, Nikolaev MA, Miliukhina IV, Bezrukova AI, Senkevich KA, Gomzyakova NA, et al. Plasma cytokine profile in synucleinophaties with dementia. J Clin Neurosci 2020;78:323–326.ArticlePubMed
- 59. Amin J, Holmes C, Dorey RB, Tommasino E, Casal YR, Williams DM, et al. Neuroinflammation in dementia with Lewy bodies: a human postmortem study. Transl Psychiatry 2020;10:267.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 60. Rathinam VA, Fitzgerald KA. Inflammasome complexes: emerging mechanisms and effector functions. Cell 2016;165:792–800.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 61. Piancone F, Saresella M, La Rosa F, Marventano I, Meloni M, Navarro J, et al. Inflammatory responses to monomeric and aggregated α-synuclein in peripheral blood of Parkinson disease patients. Front Neurosci 2021;15:639646.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 62. Duffy MF, Collier TJ, Patterson JR, Kemp CJ, Luk KC, Tansey MG, et al. Lewy body-like alpha-synuclein inclusions trigger reactive microgliosis prior to nigral degeneration. J Neuroinflammation 2018;15:129.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 63. Earls RH, Menees KB, Chung J, Barber J, Gutekunst CA, Hazim MG, et al. Intrastriatal injection of preformed alpha-synuclein fibrils alters central and peripheral immune cell profiles in non-transgenic mice. J Neuroinflammation 2019;16:250.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 64. Sacino AN, Brooks M, McKinney AB, Thomas MA, Shaw G, Golde TE, et al. Brain injection of α-synuclein induces multiple proteinopathies, gliosis, and a neuronal injury marker. J Neurosci 2014;34:12368–12378.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 65. Thakur P, Breger LS, Lundblad M, Wan OW, Mattsson B, Luk KC, et al. Modeling Parkinson’s disease pathology by combination of fibril seeds and α-synuclein overexpression in the rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017;114:E8284–E8293.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 66. Zhang W, Wang T, Pei Z, Miller DS, Wu X, Block ML, et al. Aggregated α-synuclein activates microglia: a process leading to disease progression in Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J 2005;19:533–542.ArticlePubMed
- 67. Chung HK, Ho HA, Pérez-Acuña D, Lee SJ. Modeling α-synuclein propagation with preformed fibril injections. J Mov Disord 2019;12:139–151.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 68. Kim YE, Lai TT, Kim YJ, Jeon B. Preferential microglial activation associated with pathological alpha synuclein transmission. J Clin Neurosci 2020;81:469–476.ArticlePubMed
- 69. Subbarayan MS, Hudson C, Moss LD, Nash KR, Bickford PC. T cell infiltration and upregulation of MHCII in microglia leads to accelerated neuronal loss in an α-synuclein rat model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 2020;17:242.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 70. Lee HJ, Suk JE, Patrick C, Bae EJ, Cho JH, Rho S, et al. Direct transfer of α-synuclein from neuron to astroglia causes inflammatory responses in synucleinopathies. J Biol Chem 2010;285:9262–9272.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 71. Codolo G, Plotegher N, Pozzobon T, Brucale M, Tessari I, Bubacco L, et al. Triggering of inflammasome by aggregated α-synuclein, an inflammatory response in synucleinopathies. PLoS One 2013;8:e55375.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 72. Stefanova N, Fellner L, Reindl M, Masliah E, Poewe W, Wenning GK. Toll-like receptor 4 promotes α-synuclein clearance and survival of nigral dopaminergic neurons. Am J Pathol 2011;179:954–963.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 73. Fellner L, Irschick R, Schanda K, Reindl M, Klimaschewski L, Poewe W, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 is required for α-synuclein dependent activation of microglia and astroglia. Glia 2013;61:349–360.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 74. Choi I, Zhang Y, Seegobin SP, Pruvost M, Wang Q, Purtell K, et al. Microglia clear neuron-released α-synuclein via selective autophagy and prevent neurodegeneration. Nat Commun 2020;11:1386.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 75. Kim C, Kwon S, Iba M, Spencer B, Rockenstein E, Mante M, et al. Effects of innate immune receptor stimulation on extracellular α-synuclein uptake and degradation by brain resident cells. Exp Mol Med 2021;53:281–290.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 76. Gu H, Yang X, Mao X, Xu E, Qi C, Wang H, et al. Lymphocyte activation gene 3 (Lag3) contributes to α-synucleinopathy in α-synuclein transgenic mice. Front Cell Neurosci 2021;15:656426.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 77. Mao X, Ou MT, Karuppagounder SS, Kam TI, Yin X, Xiong Y, et al. Pathological α-synuclein transmission initiated by binding lymphocyte-activation gene 3. Science 2016;353:aah3374.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 78. Juul-Madsen K, Qvist P, Bendtsen KL, Langkilde AE, Vestergaard B, Howard KA, et al. Size-selective phagocytic clearance of fibrillar α-synuclein through conformational activation of complement receptor 4. J Immunol 2020;204:1345–1361.ArticlePubMed
- 79. Sarkar S, Nguyen HM, Malovic E, Luo J, Langley M, Palanisamy BN, et al. Kv1.3 modulates neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. J Clin Invest 2020;130:4195–4212.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 80. Li N, Stewart T, Sheng L, Shi M, Cilento EM, Wu Y, et al. Immunoregulation of microglial polarization: an unrecognized physiological function of α-synuclein. J Neuroinflammation 2020;17:272.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 81. Harms AS, Cao S, Rowse AL, Thome AD, Li X, Mangieri LR, et al. MHCII is required for α-synuclein-induced activation of microglia, CD4 T cell proliferation, and dopaminergic neurodegeneration. J Neurosci 2013;33:9592–9600.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 82. Williams GP, Schonhoff AM, Jurkuvenaite A, Gallups NJ, Standaert DG, Harms AS. CD4 T cells mediate brain inflammation and neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2021;144:2047–2059.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 83. Iba M, Kim C, Sallin M, Kwon S, Verma A, Overk C, et al. Neuroinflammation is associated with infiltration of T cells in Lewy body disease and α-synuclein transgenic models. J Neuroinflammation 2020;17:214.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 84. Kam TI, Hinkle JT, Dawson TM, Dawson VL. Microglia and astrocyte dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 2020;144:105028.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 85. Stefanis L, Emmanouilidou E, Pantazopoulou M, Kirik D, Vekrellis K, Tofaris GK. How is alpha-synuclein cleared from the cell? J Neurochem 2019;150:577–590.ArticlePubMed
- 86. Lee HJ, Suk JE, Bae EJ, Lee SJ. Clearance and deposition of extracellular α-synuclein aggregates in microglia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008;372:423–428.ArticlePubMed
- 87. Loria F, Vargas JY, Bousset L, Syan S, Salles A, Melki R, et al. α-synuclein transfer between neurons and astrocytes indicates that astrocytes play a role in degradation rather than in spreading. Acta Neuropathol 2017;134:789–808.ArticlePubMed
- 88. Tsunemi T, Ishiguro Y, Yoroisaka A, Valdez C, Miyamoto K, Ishikawa K, et al. Astrocytes protect human dopaminergic neurons from α-synuclein accumulation and propagation. J Neurosci 2020;40:8618–8628.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 89. Moehle MS, West AB. M1 and M2 immune activation in Parkinson’s disease: foe and ally? Neuroscience 2015;302:59–73.ArticlePubMed
- 90. Kim C, Ho DH, Suk JE, You S, Michael S, Kang J, et al. Neuron-released oligomeric α-synuclein is an endogenous agonist of TLR2 for paracrine activation of microglia. Nat Commun 2013;4:1562.ArticlePubMed
- 91. Elabi O, Gaceb A, Carlsson R, Padel T, Soylu-Kucharz R, Cortijo I, et al. Human α-synuclein overexpression in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease leads to vascular pathology, blood brain barrier leakage and pericyte activation. Sci Rep 2021;11:1120.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 92. Earls RH, Menees KB, Chung J, Gutekunst CA, Lee HJ, Hazim MG, et al. NK cells clear α-synuclein and the depletion of NK cells exacerbates synuclein pathology in a mouse model of α-synucleinopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020;117:1762–1771.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 93. George S, Tyson T, Rey NL, Sheridan R, Peelaerts W, Becker K, et al. T cells limit accumulation of aggregate pathology following intrastriatal injection of α-synuclein fibrils. J Parkinsons Dis 2021;11:585–603.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 94. Xia Y, Zhang G, Kou L, Yin S, Han C, Hu J, et al. Reactive microglia enhance the transmission of exosomal α-synuclein via toll-like receptor 2. Brain 2021;144:2024–2037.ArticlePubMed
- 95. Izco M, Blesa J, Verona G, Cooper JM, Alvarez-Erviti L. Glial activation precedes alpha-synuclein pathology in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Res 2021;170:330–340.ArticlePubMed
- 96. Rostami J, Holmqvist S, Lindström V, Sigvardson J, Westermark GT, Ingelsson M, et al. Human astrocytes transfer aggregated alpha-synuclein via tunneling nanotubes. J Neurosci 2017;37:11835–11853.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 97. Ngolab J, Trinh I, Rockenstein E, Mante M, Florio J, Trejo M, et al. Brain-derived exosomes from dementia with Lewy bodies propagate α-synuclein pathology. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2017;5:46.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 98. Liddelow SA, Guttenplan KA, Clarke LE, Bennett FC, Bohlen CJ, Schirmer L, et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017;541:481–487.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 99. Yun SP, Kam TI, Panicker N, Kim S, Oh Y, Park JS, et al. Block of A1 astrocyte conversion by microglia is neuroprotective in models of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Med 2018;24:931–938.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 100. Niu H, Wang Q, Zhao W, Liu J, Wang D, Muhammad B, et al. IL-1β/IL-1R1 signaling induced by intranasal lipopolysaccharide infusion regulates α-synuclein pathology in the olfactory bulb, substantia nigra and striatum. Brain Pathol 2020;30:1102–1118.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 101. La Vitola P, Balducci C, Baroni M, Artioli L, Santamaria G, Castiglioni M, et al. Peripheral inflammation exacerbates α-synuclein toxicity and neuropathology in Parkinson’s models. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2021;47:43–60.ArticlePubMed
- 102. Sommer A, Fadler T, Dorfmeister E, Hoffmann AC, Xiang W, Winner B, et al. Infiltrating T lymphocytes reduce myeloid phagocytosis activity in synucleinopathy model. J Neuroinflammation 2016;13:174.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 103. Wang X, Chi J, Huang D, Ding L, Zhao X, Jiang L, et al. α-synuclein promotes progression of Parkinson’s disease by upregulating autophagy signaling pathway to activate NLRP3 inflammasome. Exp Ther Med 2019;19:931–938.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 104. Wang Y, Wang Q, Yu R, Zhang Q, Zhang Z, Li H, et al. Minocycline inhibition of microglial rescues nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurodegeneration caused by mutant alpha-synuclein overexpression. Aging (Albany NY) 2020;12:14232–14243.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 105. Vidal-Martínez G, Vargas-Medrano J, Gil-Tommee C, Medina D, Garza NT, Yang B, et al. FTY720/fingolimod reduces synucleinopathy and improves gut motility in A53T mice: contributions of pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Pro-BDNF) and mature BDNF. J Biol Chem 2016;291:20811–20821.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 106. Wang L, Hong J, Wu Y, Liu G, Yu W, Chen L. Seipin deficiency in mice causes loss of dopaminergic neurons via aggregation and phosphorylation of α-synuclein and neuroinflammation. Cell Death Dis 2018;9:440.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 107. NINDS Exploratory Trials in Parkinson Disease (NET-PD) FS-ZONE Investigators. Pioglitazone in early Parkinson’s disease: a phase 2, multicentre, double-blind, randomised trial. Lancet Neurol 2015;14:795–803.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 108. Kwon OC, Song JJ, Yang Y, Kim SH, Kim JY, Seok MJ, et al. SGK1 inhibition in glia ameliorates pathologies and symptoms in Parkinson disease animal models. EMBO Mol Med 2021;13:e13076.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 109. Kim C, Spencer B, Rockenstein E, Yamakado H, Mante M, Adame A, et al. Immunotherapy targeting toll-like receptor 2 alleviates neurodegeneration in models of synucleinopathy by modulating α-synuclein transmission and neuroinflammation. Mol Neurodegener 2018;13:43.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 110. Churchill MJ, Cantu MA, Kasanga EA, Moore C, Salvatore MF, Meshul CK. Glatiramer acetate reverses motor dysfunction and the decrease in tyrosine hydroxylase levels in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2019;414:8–27.ArticlePubMed
- 111. Gendelman HE, Zhang Y, Santamaria P, Olson KE, Schutt CR, Bhatti D, et al. Evaluation of the safety and immunomodulatory effects of sargramostim in a randomized, double-blind phase 1 clinical Parkinson’s disease trial. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 2017;3:10.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 112. Gordon R, Albornoz EA, Christie DC, Langley MR, Kumar V, Mantovani S, et al. Inflammasome inhibition prevents α-synuclein pathology and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mice. Sci Transl Med 2018;10:eaah4066.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 113. Leem YH, Park JS, Park JE, Kim DY, Kang JL, Kim HS. Papaverine inhibits α-synuclein aggregation by modulating neuroinflammation and matrix metalloproteinase-3 expression in the subacute MPTP/P mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother 2020;130:110576.ArticlePubMed
- 114. Wang W, Nguyen LT, Burlak C, Chegini F, Guo F, Chataway T, et al. Caspase-1 causes truncation and aggregation of the Parkinson’s disease-associated protein α-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016;113:9587–9592.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 115. Bassil F, Fernagut PO, Bezard E, Pruvost A, Leste-Lasserre T, Hoang QQ, et al. Reducing C-terminal truncation mitigates synucleinopathy and neurodegeneration in a transgenic model of multiple system atrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016;113:9593–9598.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 116. Wang MX, Cheng XY, Jin M, Cao YL, Yang YP, Wang JD, et al. TNF compromises lysosome acidification and reduces α-synuclein degradation via autophagy in dopaminergic cells. Exp Neurol 2015;271:112–121.ArticlePubMed
- 117. Barnum CJ, Chen X, Chung J, Chang J, Williams M, Grigoryan N, et al. Peripheral administration of the selective inhibitor of soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF) XPro(R)1595 attenuates nigral cell loss and glial activation in 6-OHDA hemiparkinsonian rats. J Parkinsons Dis 2014;4:349–360.ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Recent advances of nanomaterials for intervention in Parkinson’s disease in the context of anti-inflammation
Ruoyu Zhang, Xiaotong Chen, Yuanyuan Cheng, Zixuan Chen, Xiaoqiong Li, Yulin Deng
Coordination Chemistry Reviews.2024; 502: 215616. CrossRef - Microglial inhibition alleviates alpha-synuclein propagation and neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease mouse model
Thuy Thi Lai, Young Eun Kim, Linh Thi Nhat Nguyen, Tinh Thi Nguyen, In Hee Kwak, Franziska Richter, Yun Joong Kim, Hyeo-il Ma
npj Parkinson's Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - New Insights into Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Eveljn Scarian, Camilla Viola, Francesca Dragoni, Rosalinda Di Gerlando, Bartolo Rizzo, Luca Diamanti, Stella Gagliardi, Matteo Bordoni, Orietta Pansarasa
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(5): 2698. CrossRef - Neuroinflammation following anti-parkinsonian drugs in early Parkinson’s disease: a longitudinal PET study
Tatsuhiro Terada, Tomoyasu Bunai, Takanori Hashizume, Takashi Matsudaira, Masamichi Yokokura, Hirotsugu Takashima, Takashi Konishi, Tomokazu Obi, Yasuomi Ouchi
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Neuroinflammation and Immune Dysfunction in the Mechanisms of Development of Parkinson’s Disease
G. V. Idova, E. L. Alperina, S. Ya. Zhanaeva
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology.2023; 53(9): 1534. CrossRef - Vitamin D3 actions on astrocyte cells: A target for therapeutic strategy in Parkinson’s disease?
Erlânia Alves de Siqueira, Emanuel Paula Magalhães, Ramon Róseo Paula Pessoa Bezerra de Menezes, Tiago Lima Sampaio, Danya Bandeira Lima, Conceição da Silva Martins, Kelly Rose Tavares Neves, Gerly Anne de Castro Brito, Alice Maria Costa Martins, Glauce S
Neuroscience Letters.2023; 793: 136997. CrossRef - ASC specks exacerbate α‑synuclein pathology via amplifying NLRP3 inflammasome activities
Ran Zheng, Yiqun Yan, Shaobing Dai, Yang Ruan, Ying Chen, Chenjun Hu, Zhihao Lin, Naijia Xue, Zhe Song, Yi Liu, Baorong Zhang, Jiali Pu
Journal of Neuroinflammation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Neuroinflammation and Related Mitochondrial Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease
Qiu-Qin Han, Weidong Le
Neuroscience Bulletin.2023; 39(5): 832. CrossRef - The Role of Ubiquitin–Proteasome System and Mitophagy in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease
Yu Liang, Guangshang Zhong, Mingxin Ren, Tingting Sun, Yangyang Li, Ming Ye, Caiyun Ma, Yu Guo, Changqing Liu
NeuroMolecular Medicine.2023; 25(4): 471. CrossRef - Anethole attenuates motor dysfunctions, striatal neuronal activity deficiency and blood brain barrier permeability by decreasing striatal α-synuclein and oxidative stress in rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease of male rats
Sadegh Moradi Vastegani, Seyed Esmaeil Khoshnam, Samireh Ghafouri, Nima Bakhtiari, Yaghoob Farbood, Alireza Sarkaki, Wesley Lyeverton Correia Ribeiro
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(11): e0294612. CrossRef - A2A Adenosine Receptor Antagonists: Are Triazolotriazine and Purine Scaffolds Interchangeable?
Andrea Spinaci, Catia Lambertucci, Michela Buccioni, Diego Dal Ben, Claudia Graiff, Maria Cristina Barbalace, Silvana Hrelia, Cristina Angeloni, Seyed Khosrow Tayebati, Massimo Ubaldi, Alessio Masi, Karl-Norbert Klotz, Rosaria Volpini, Gabriella Marucci
Molecules.2022; 27(8): 2386. CrossRef - Oligomeropathies, inflammation and prion protein binding
Gianluigi Forloni, Pietro La Vitola, Claudia Balducci
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
Comments on this article
 KMDS
KMDS
 E-submission
E-submission
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite




